SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java
Introduction
HP NonStop SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java—523726-003
1-16
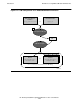
Default Processing Without Module Definition Files
SQL Compilation
The SQL/MX compiler (MXCMP) performs these specific functions during SQL
compilation:
•
Checks database object references to verify their existence
•
Expands view definitions (that is, replaces a view name with a SELECT statement)
•
Determines an optimized execution plan and access path for each DML statement
if the database objects in the statement are present at SQL compile time
•
Generates executable code for the execution plans if the database objects in the
statement are present at SQL compile time and creates an SQL/MX module in the
/usr/tandem/sqlmx/USERMODULES directory
•
Generates a list of the SQL statements in the program file, including messages
•
Returns a completion code indicating the outcome of the compilation
At run time, the SQL/MX executor invokes the SQL/MX compiler to compile dynamic
SQL statements and to recompile any static SQL statements that refer to database
objects that have changed and that affect the execution plan of the statement. If a
program accesses a table whose definition has changed since the last static SQL
compilation, you should recustomize and statically recompile the program to improve
performance. For more information, see Similarity Checks and Automatic
Recompilation on page 4-26.
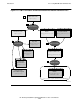
Module
The SQL/MX compiler compiles and optimizes the embedded SQL statements in a
module definition to produce a compiled SQL/MX module.
The module contains the execution plans of SQL statements and resides in the
/usr/tandem/sqlmx/USERMODULES directory.
You can view the contents of the module by using the EXPLAIN function. For more
information, see Displaying Query Execution Plans on page 5-46.
Note. Do not confuse module files, which do not have file extensions and reside in the
/usr/tandem/sqlmx/USERMODULES directory, with module definition files (.m), which are
optionally generated during SQLJ processing and are precursors to modules. For more
information, see Module Definition File
on page 1-19.
Note. Currently, SQL/MX does not support locally placed modules for SQLJ applications. The
modules of an SQLJ application must be stored in the /usr/tandem/sqlmx/USERMODULES
directory. Otherwise, the program will either run dynamically or return an SQL exception
indicating that the module is missing or corrupted. For more information, see SQL/MX
Compiler Errors on page 4-5.