SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java
Introduction
HP NonStop SQL/MX Programming Manual for Java—523726-003
1-19
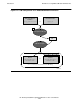
Processing With Module Definition Files
Customization With Module Definition Files
After successful translation and Java compilation, the SQLJ translator program
automatically invokes customization of the profiles (.ser) for SQL/MX. Specifying
-createMDF=true (or -SQLMXCustomizerVersion=800) on the SQLJ command
line or in a properties file causes the SQLJ customizer to produce a module definition
file (.m) in addition to storing the embedded module definition in the extended profile.
See -createMDF on page 5-28 (or -SQLMXCustomizerVersion on page 5-26).
The SQLJ customizer computes a form of each SQL statement that is ready for the
SQL/MX compiler (MXCMP) and writes it to the module definition file (.m). The other
functions of the customizer are the same as the default method of SQLJ processing.
For details, see Customization Without Module Definition Files on page 1-13.
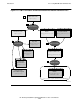
Module Definition File
The customizer uses each profile and the metadata information of each embedded
SQL statement in the profile to generate a module definition file (.m). The module
definition file contains a form of each SQL statement that is ready to be compiled by
the SQL/MX compiler and SQL/MX-specific information related to each embedded
SQL statement, such as the procedure header and the input and output descriptor
declarations.
Extended Profile
The customizer extends the profile (.ser file) with SQL/MX-customized run-time
information, producing an extended profile. For more information, see Extended Profile
on page 1-13.
Compilation by the SQL/MX Compiler (MXCMP)
After customization, the SQLJ translator program automatically invokes SQL
compilation. The SQL/MX compiler (or the mxcmp command) compiles and optimizes
the embedded SQL statements in the module definition file (.m) to produce a compiled
SQL/MX module. The module contains the execution plans of the SQL statements.
The SQL/MX compiler performs the same functions when invoked by the SQLJ
translator as when the mxCompileUserModule utility invokes it. For details, see SQL
Compilation on page 1-16 and Module on page 1-16.
Note. Do not confuse module definition files (.m), which are optionally generated during SQLJ
processing and are precursors to modules, with module files, which do not have file extensions
and reside in the /usr/tandem/sqlmx/USERMODULES directory. For more information, see
Module on page 1-16.
Note. Currently, SQL/MX does not support locally placed modules for SQLJ applications. The
modules of an SQLJ application must be stored in the /usr/tandem/sqlmx/USERMODULES
directory. Otherwise, the program will either run dynamically or return an SQL exception
indicating that the module is missing or corrupted. For more information, see SQL/MX
Compiler Errors on page 4-5.
4
5