TAL Programmer's Guide
Equivalencing Structure Pointers
Using Equivalenced Variables
10–18 096254 Tandem Computers Incorporated
Avoid Mixing Addressing Modes
All guidelines for avoiding mixed address modes given earlier in this section apply
to equivalenced structure pointers.
Accessing Data Through
Equivalenced Structure
Pointers
To access a structure through a structure pointer, qualify the name of the pointer
with the appropriate structure item names, as was described in Section 9, “Using
Pointers.”
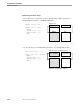
This example accesses item A[2] in structure STR through structure pointer PTR:
Primary area
ptr to STR
STRUCT .str;
BEGIN
INT a[0:3];
INT b[0:9];
END;
INT .ptr (str) = str;
ptr.a[2] := %14;
!Assign value to
! STR.A[2]
PTR.A[2]
STR
322
Secondary area
.
.
.
.
.
.
Avoiding an Access Error
As previously discussed, you can equivalence a structure pointer to an indirect
structure. Both the structure pointer and the implicit pointer to the indirect structure
then point to the data of the structure.
Primary area
INT var1;
INT var2;
STRUCT .str;
BEGIN
INT a[0:3];
INT b[0:9];
END;
INT .ptr (str) = str;
Secondary area
VAR2
ptr to STR
PTR
STR
.
.
.
VAR1G[0]
323
.
.
.