Tandem Logon Manager for IBM Systems (ILOGMGR) Manual
Tandem Logon Manager for IBM Systems (ILOGMGR) Manual—127335 1-1
1
Introduction to the ILOGMGR
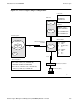
The Tandem Logon Manager for IBM Systems (ILOGMGR) allows dependent
logical units, such as 3270-type terminals, to gain access to applications running on a
Tandem system by using a logon procedure.
The ILOGMGR is an application program for the Virtual Telecommunications Access
Method (VTAM) that uses standard VTAM programming interfaces to receive logon
requests from dependant LUs requesting sessions with Tandem applications.
Dependant LUs cannot initiate sessions, but they can issue logon requests to the
ILOGMGR. The ILOGMGR forwards the logon request to the Tandem system, which
directs the requested application to initiate a session with the dependant LU. Once this
session is initiated, the ILOGMGR terminates its session with the dependant LU and is
no longer involved.
The ILOGMGR is managed by a control file that defines the following local
information:
•
The VTAM APPL name of the ILOGMGR
•
All applicable SNAX/APN logon manager (TLOGMGR) LU names
•
The supported Tandem application names
•
A routing code for messages
•
A request timeout value, which specifies the time period that the ILOGMGR waits
for responses to Program Start Requests sent to a TLOGMGR LU
•
A retry open value, which specifies the time the ILOGMGR waits before retrying
opening an access method control block (ACB)
See Section 3, “Configuring for the ILOGMGR,” for information about configuring the
control file.
The ILOGMGR communicates over an SNA session with the logon manager
(TLOGMGR) component of SNAX/APN. The TLOGMGR accepts and responds to
session-initiation requests and interfaces to Tandem application programs.
The ILOGMGR functions on any IBM or IBM-compatible host processor running the
Multiple Virtual Storage (MVS) operating system. This manual refers to either
processor as “the SNA host.”
Multiple ILOGMGRs, TLOGMGRs, and SNAX/APN lines may be configured under
certain circumstances. Detailed information about these special-case configurations can
be found in Section 3, “Configuring for the ILOGMGR.”