Tandem Logon Manager for IBM Systems (ILOGMGR) Manual
Tandem Logon Manager for IBM Systems (ILOGMGR) Manual—127335 3-1
3
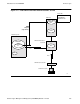
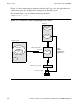
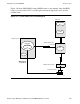
Configuring for the ILOGMGR
This section describes how to configure your environment to use the ILOGMGR. You
need to configure the following items:
•
The control file, which supports the ILOGMGR
•
The VTAM list, which supports VTAM
•
The NCP configuration, which supports the SNA communication controller
This section also describes how to configure a system for multiple ILOGMGRs,
TLOGMGRs, SNAX/APN lines, or some combination of the three.
Also included in this section are examples showing you how to configure your
environment for the ILOGMGR when you are using Token-Ring.
Configuring the Control File
The control file is a sequential, fixed-record-length data set that defines the following
items in the form of control records. Further information about these control records
appears later in this section.
•
The ILOGMGR VTAM APPL name
•
The SNAX/APN logon manager (TLOGMGR) names
•
The supported Tandem application names (TDMAPPLS)
•
A routing code for messages
•
A request timeout value
•
A value representing the amount of time the ILOGMGR waits before retrying
opening an access method control block (ACB).
Control file records may be any length up to 256 bytes, but the ILOGMGR reads only
columns 1 through 72.
Comment fields may appear in a control file record if separated from the operands by a
space. The control file also may contain entire comment records. These records start
with either an asterisk (*) or exclamation mark (!) in the first column.
At execution of the ILOGMGR, a data definition statement (DD statement) must be
supplied, which uses a data definition name (DDNAME) of CTLIN to represent the
control file.
A DD card that includes a DDNAME of “CTLOUT” in the ILOGMGR execution JCL
stream directs all ILOGMGR messages to a user-defined data set. See “Using a
CTLOUT Data Set,” later in this section for details.