TCP/IP (Parallel Library) Configuration and Management Manual
Introduction
HP NonStop TCP/IP (Parallel Library) Configuration and Management Manual—522271-006
2-10
TCPMAN
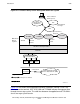
Note that in Parallel Library TCP/IP, the TCPMON, TCPLIB and application
components are in the data path. Figure 2-3 also shows that the TCP/IP library is
pulled into the application context. Data transfer in the Parallel Library TCP/IP occurs
within the library.
The conventional TCP/IP environment shown in Figure 2-3 requires two
message-system, inter-process, communication transfers.
TCPMAN
The manager process (TCPMAN) runs as a process pair and is the management point
for the Parallel Library TCP/IP subsystem. Only one manager process pair exists for
each system. TCPMAN is always named $ZZTCP. Once the monitors (TCPMON, see
below) have been configured at least once in the system, TCPMAN starts the monitors
along with any other subordinate objects from the system configuration database
whenever TCPMAN is started.
TCPMAN automatically configures one TCPMON for each system as the MASTER
TCPMON. The MASTER TCPMON is usually the first TCPMON started. If the MASTER
TCPMON processor fails, TCPMAN picks the TCPMON in the next configured
processor as the MASTER. TCPMAN ensures one MASTER TCPMON always exists in
the system.
Figure 2-3. Data Path Comparison: Conventional vs. Parallel Library TCP/IP
VST0203.vsd
LAN Drivers/Interrupt Handlers
TCPLIB
Outbound
Packets
Inbound
Packets
Parallel Library TCP/IP
Application
G06 TCP/IP
Process
SLSA DIH
Conventional TCP/IP
Inbound/Outbound
Packets
Inbound/Outbound
Packets
Legend
Message system inter-process transfer
Data transfer within the library
TCPMON
Application