TCP/IP (Parallel Library) Configuration and Management Manual
Introduction
HP NonStop TCP/IP (Parallel Library) Configuration and Management Manual—522271-006
2-13
QIO
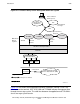
Library TCP/IP subsystem and its relationship to the QIO and SLSA subsystems. The
LAN drivers/interrupt handlers and the LAN adapters (for example, G4SA) are part of
the SLSA subsystem. The Parallel Library TCP/IP subsystem components and part of
the application run in the QIO shared memory segment.
QIO
The QIO subsystem has been enhanced as of G06.17 to allow you to have more
control over certain aspects of memory management. You can now configure QIO to
run in the Kseg2 memory segment and you can also control where QIO runs in the flat
memory segment. Configuring QIO to run in Kseg2 can improve performance for
Parallel Library TCP/IP but also imposes constraints that affect all QIO clients
(including Parallel Library TCP/IP). As discussed in the QIO Configuration and
Management Manual, you must consider these constraints as well as a variety of other
factors before changing the default QIO configuration.
Some of the constraints affecting Parallel Library TCP/IP (as well as other QIO clients)
include the reduction of QIO memory space to 128 MB when QIO is moved to Kseg2.
This impacts the number of LIFs that you can configure on your system because LIFs
use QIO memory. It also impacts the number of sockets that can be opened because
open sockets use QIO memory as well. 128 MB may not be sufficient for your Parallel
Library TCP/IP or other QIO client needs.
For details about planning for and using the new QIO features, see the QIO
Configuration and Management Manual.
Note. The default configuration for the QIO subsystem has not changed.
Note. Whether you use the default QIO configuration or one of the newly supported custom
configurations, you do not need to change anything in Parallel Library TCP/IP; all changes are
made in the QIO subsystem.