TCP/IPv6 Configuration and Management Manual (G06.29+, H06.03+, J06.03+)
Example Illustrations and Adding Features to the
Basic Configuration
HP NonStop TCP/IPv6 Configuration and Management Manual—524523-012
5-2
DUAL Mode
In this configuration, you can configure applications so that they are restricted to
listening to IP addresses 172.14.217.25 and 172.14.200.24, the configured LNPs. All
other applications can share the default LNP represented by $ZSAM1.
For background information about this feature, see Logical-Network Partitioning (LNP)
on page 2-7.
DUAL Mode
Example 1-7 on page 1-15 shows how to configure the subsystem for IPv6 and IPv4
communications. This configuration is shown in Figure 5-2.
This example shows that:
When the monitors are configured for DUAL mode, the NonStop TCP/IPv6
subsystem automatically adds a tunnel for IPv4-network communications. The
tunnel is a SUBNET named TUN of TYPE TUNNEL. As soon as an IPv4 SUBNET is
added to the system, this tunnel becomes operational and applications selecting a
TCP6SAM process can communicate over both IPv4 and IPv6 networks. As this
process is automated, in the examples in Section 1, Quick Start, you do not see
the explicit addition of a tunnel SUBNET.
The examples in Section 1, Quick Start all use Stateless address
autoconfiguration. When using NonStop TCP/IPv6 in DUAL mode, you must assign
an IPv4 IP address to the SUBNET but the IPv6 addresses are automatically
assigned.
The host automatically assigns IPv6 link-local addresses to all SUBNETs and, as
long as a router that supports the Neighbor Discovery Protocol is available on the
network, the host also assigns IPv6 global addresses.
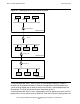
Figure 5-2. Dual-Mode Host, Example 1-7
Host, Dual Mode
172.14.215.27
Automatically assigned IPv6
address
VST134.vsd
TUN
IPv4 Host
IPv6 Host
IPv4/6 Network
Encapsulated packets