TCP/IPv6 Configuration and Management Manual (G06.29+, H06.03+, J06.03+)
Overview of NonStop TCP/IPv6
HP NonStop TCP/IPv6 Configuration and Management Manual—524523-012
2-4
Single IP
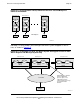
By eliminating message-system hops, NonStop TCP/IPv6 reduces the total path length
from the application to the wire. This path-length reduction reduces individual request
latency. In addition, throughput is higher because more requests can be serviced each
second without increasing processor cost.
Single IP
In conventional TCP/IP, you had a limited ability to scale a listening application; if you
wanted to run different instances of the application in different processors and using
different TCP/IP processes, you would have to do so on different IP addresses. Each
TCP/IP process appeared as a unique IP host to the outside world, as shown in
Figure 2-3
on page 2-5.
Figure 2-2. Conventional TCP/IP Requires a Message-System Inter-Process Hop
Web
1
Web
2
TCP/IP 1
TCP/IP 2 TCP/IP 16
Web
16
Message-System
Inter-Process
Hop
Processor 0 Processor 1 Processor 15
Message-System
Inter-Process
Hop
VST120.vsd
LAN
Adapters