TCP/IPv6 Configuration and Management Manual (G06.29+, H06.03+, J06.03+)
Maximize the Benefit of the NonStop TCP/IPv6
Architecture
HP NonStop TCP/IPv6 Configuration and Management Manual—524523-012
3-6
Distributor Listening Model
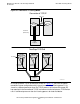
In the NonStop TCP/IPv6 environment, with round-robin filtering enabled, you can
have multiple copies of the monolithic listener running in different processors, all
sharing the same port (shown in Figure 3-2 on page 3-5). As round-robin filtering is
enabled, the adapter distributes the incoming connections to the different listening
processes, and the listening processes, in a sense, “distribute” those connections
within its own process by creating sockets for each connection. An example of how this
type of dual-layer distribution could work is described in these steps:
1. The first incoming connection request goes to the listening process in the first
processor and the listening process creates a socket for the connection.
2. The second connection request goes to the listening process in the second
processor and the listening process creates a socket for the connection.
3. The third connection request goes to the listening process in the third processor
and the listening process creates a socket for the connection.
4. The fourth connection request goes to the listening process in the first processor
and the listening process creates a second socket for that connection.
5. The fifth connection request goes to the listening process in the second processor
and the listening process creates a second socket for that connection.
In summary, you can use the NonStop TCP/IPv6 feature of all processors having
access to one adapter to scale your monolithic listener server process (by adding more
processes in different processors and distributing the work load among them), and
eliminate an IPC hop between the server process and the TCP/IP process (which
increases transmission speed).
Configuration Example for the Monolithic Listening Model on page 3-14 explains how
to configure this listener model.
Distributor Listening Model
This method uses an interface process which serves as a distributor by using NonStop
operating system inter-process communication (IPC) to talk to multiple back-end server
instances. In this method, the distributor binds to a well-known port and then accepts
multiple connections by creating a socket for each connection. The distributor listener
then performs the accepts, sends, receives, and so on, on those sockets, on behalf of
the back-end servers. The distributor handles all data flow and control, and forwards
the received data using NonStop OS inter-process communication to back-end server
processes. A good example of this method is a TCP/IP application developed for the
Pathway environment.
The Pathway environment provides a rich set of server process-management facilities
and load-balancing facilities. A front-end distributor process using a set of verbs
collectively referred to as PATHSEND, communicates with the back-end servers.
PATHSEND allows load-balancing algorithms to distribute the data to the back-end
server instances.