TMF Application Programmer's Guide (G06.26+)
Designing Single-Threaded Processes
HP NonStop TMF Application Programmer’s Guide—522419-005
2-11
Single-Threaded Servers
as a primary) should call ABORTTRANSACTION, start a new backup process, and
then restart the transaction using the checkpointed application data.
If RESUMETRANSACTION returns no error, TMF has not yet sufficiently processed
the failure of the primary process to indicate that the transaction aborted. The
application should call ABORTTRANSACTION, start a new backup process, and
restart the transaction using checkpointed application data.
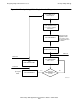
Single-Threaded Servers
Within the TMF programming environment, a server is an application program module
that manipulates a database in response to work requests from a requester.
A single-threaded server can work on behalf of only one transaction at a time: having
accepted a work request for one transaction, a single-threaded server cannot accept
another work request until it has completed all of its work for the current request.
Applicable System Procedures
Single-threaded TMF servers use the following file system procedures:
•
ABORTTRANSACTION—aborts the current transaction
•
CLOSE—closes $RECEIVE or a subordinate server process
•
LASTRECEIVE—obtains the tag value associated with a work request (this
procedure call must immediately follow the READUPDATE call that accepted the
particular work request)
•
FILE_OPEN_—opens $RECEIVE or a subordinate server process
•
READUPDATE—accepts an incoming work request from a requester
•
REPLY—sends a reply message to a requester
•
RESUMETRANSACTION (0)—sets the current transaction to the nil state
•
ACTIVATERECEIVETRANSID (tag)—resets the current transaction from the nil
state to the transaction identifier of the work request identified by the specified tag
value
•
WRITEREAD—sends a work request to a subordinate server process and accepts
a reply from the server
Note. In addition to the transaction inherited from a requester, a single-threaded server
can initiate a new transaction by issuing a BEGINTRANSACTION call. If, however, the server
attempts to issue a second BEGINTRANSACTION call without first issuing either an
ENDTRANSACTION or ABORTTRANSACTION call, an error 83 occurs.