TMF Application Programmer's Guide (G06.26+)
Designing Multithreaded Processes
HP NonStop TMF Application Programmer’s Guide—522419-005
3-8
Checkpointing Strategy
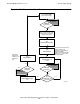
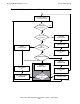
Figure 3-3. Multithreaded Requester; Detailed Functionality
Restarting Aborted Transactions on Takeover
If the primary requester fails for any reason, the backup process automatically takes
over. When that happens, the backup process must determine which of the active
transactions were successfully committed before the failure occurred, and which were
aborted.
The processing of a transaction never transfers in midstream from the primary to the
backup; any transactions that were aborted must be restarted and performed in their
entirety.
One of the items that the primary requester must maintain in local storage is a list of
the tag values associated with all active transactions. The primary process periodically
passes the tag list to the backup process using a CHECKPOINT call. In general, it is
most appropriate to do so by using the CHECKPOINT call that follows each
BEGINTRANSACTION call.
BEGIN TRANSACTION
Set up local storage with all the
application data necessary to start
the transaction.
CALL BEGINTRANSACTION.
Write the transaction tag to local
storage.
CHECKPOINT #1
Call CHECKPOINT (include the
TFILE's file number and the
transaction tag in the data list
along with the addresses of all
local data blocks necessary to
start the transaction).
CHECKPOINTS #2 and #3
Call CHECKPOINT to flush the
transaction's entry from the
TFILE (include the TFILE's file
number in the data list).
ISSUE WRITEREAD TO SERVER
Issue a nowait WRITEREAD
call to a server process.
RESUME TRANSACTION
Use the transaction tag
returned by AWAITIO in a
RESUMETRANSACTION call
to resume the transaction.
ABORT TRANSACTION
Call ABORTTRANSACTION.
Delete the transaction tag from
local storage.
END TRANSACTION
Call ENDTRANSACTION.
VST004.vsd