TS/MP Pathsend and Server Programming Manual (G06.24+, H06.03+)
Introduction to Pathway Application Programming
NonStop TS/MP Pathsend and Server Programming Manual–132500
1-17
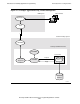
Transaction Processing Scenario
In this scenario, clerks at an order entry office enter their transactions into terminals
attached to an IBM system. Processing of the transactions, however, requires access to a
database that is linked to a Tandem NonStop system.
1. The clerks enter transactions into their terminals and initiate processing by pressing
function keys. Any preliminary checking or editing is performed by the application
on the IBM system.
2. The IBM system collects the transactions and sends them to a Pathsend requester
located on the Tandem NonStop system. The transactions are sent by using a high-
speed networking product; for example, Tandem’s SNAX Advanced Peer
Networking (SNAX/APN) product.
3. The Pathsend requester accepts the transactions for the Tandem NonStop system and
formats a request message containing the name of the server class and the data
needed by the server to complete its work. The TMF transaction begins.
4. The Pathsend requester forwards the request message to the LINKMON process by
calling the Pathsend SERVERCLASS_SEND_ procedure. (This is a context-free
message.)
5. If the LINKMON process does not have a link to the specified server class, the
LINKMON process asks the PATHMON process for a link to a server process in the
server class. The PATHMON process replies that a server process is available. If the
LINKMON process already has a link to the server class, this step is not performed.
6. The LINKMON process forwards the request to the server process by using
NonStop Kernel interprocess communication.
7. The server process receives and reads the request message.
8. Executing NonStop SQL/MP statements in its program, the server process accesses
the database and updates the appropriate information.
9. The server process formats a reply message, which verifies that the information has
been updated, and replies to the LINKMON process by using NonStop Kernel
interprocess communication.
10. The LINKMON process receives and forwards the reply messages to the Pathsend
requester. The TMF transaction ends.
11. The Pathsend requester returns the reply messages to the IBM system, where the
application displays the information on the terminal screens.