Virtual TapeServer 8.2 Configuration Guide
Table Of Contents
- Virtual TapeServer for NonStop Servers Configuration Guide
- Preface
- Introduction
- Overview of Tasks
- Reconfiguring Vaults
- Enabling Licensed Features
- Configuring Ports
- Creating and Managing VTLs and VTDs
- Enabling and Performing Tape-to-tape Exports
- Enabling and Performing Stacked Exports
- Enabling and Configuring Data Replication
- Enabling and Configuring Role Swapping
- Configuring EMS Communication
- Enabling and Configuring Data Encryption
- Creating and Managing Virtual Media
- Enabling and Configuring Scan/Cleanup
- Configuring User Accounts
- Configuring Web Interface Preferences
- Managing the VTS Server
- Troubleshooting
- Maintaining GFS for VTS
- Reinstalling and Restoring VTS
- Attaching External Devices after Initial Deployment
- TCP/IP Ports and Protocols
- Index
Maintaining GFS for VTS | 167
Troubleshooting
The following topics describe common GFS problems and their solutions.
If VTS server fails to join the cluster after reboot
If a VTS server fails to join the GFS cluster after it reboots, complete these troubleshooting
steps:
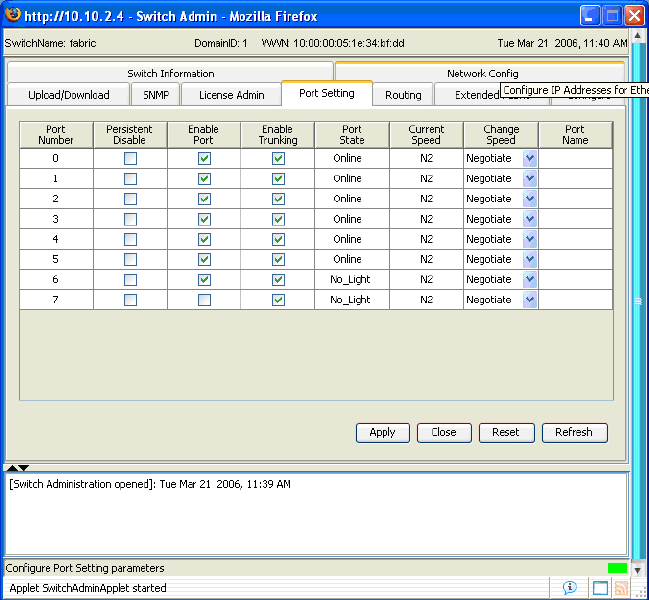
1. Check your SAN to make sure the port is enabled. Below is a MSA/Brocade example.
Make sure that the port is checked “Enable.”
2. Confirm the Fibre Channel port is available and confirm that the Linux operating system
sees the LUN defined for the file system by the storage array. This command will list all
SCSI devices. From the VTS server command line, enter this command:
[root@VTS001 root]# sg_map -x
Here is the output:
/dev/sg0 1 0 4 0 1 /dev/st0
/dev/sg1 1 0 5 0 1 /dev/st1
/dev/sg2 1 0 6 0 8
/dev/sg3 4 0 0 0 0 /dev/sda
/dev/sg4 4 0 0 1 0 /dev/sdb
/dev/sg5 4 0 0 2 0 /dev/sdc
/dev/sg6 4 0 0 3 0 /dev/sdd
/dev/sg7 4 0 0 4 0 /dev/sde










