Virtual TapeServer 8.4 Configuration Guide
Creating and Managing VTLs and VTDs | 31
After creating a VTL, you should
l create pools, which organize and set properties on all tapes in a pool
l add virtual tapes to the pools
l insert virtual tapes into the VTL
See "Managing virtual tapes" on page 96 for more information.
Managing and using VTLs
You can perform the following to manage and use VTLs in your environment:
l Modify VTLs, including adding and removing slots and VTDs
l Modify VTDs in a VTL
l Manage virtual tapes in a VTL, including inserting and replacing virtual tapes
l Delete VTLs
These procedures are provided in the help. To view the help, click the Help button at the top of any
page.
To view a list of VTLs
Click Configuration > Virtual Devices on the navigation pane.
The VIRTUAL TAPE DRIVES section lists the VTDs (standalone and those in VTLs) on the server. The
names of VTDs that are associated with VTLs are similar to the names of the VTLs.
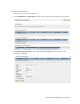
The VIRTUALTAPELIBRARIESsection lists all VTLs on the server. Here is an explanation of the
columns in the VIRTUALTAPELIBRARIESsection:
l VTL - The name of the VTL.
l Port - The port to which the host server is connected.
l Target - The SCSI ID on which the VTL will respond.
l Lun - The logical unit number, which identifies the sub-ID on the port (bus).
l Initiator - The SCSI ID of the host port to which VTS is connected.
l Serial Num - The serial number of the VTL.
l Tape Type - The type of library that the VTL emulates.
l WWPN - The World Wide Port Name, which uniquely identifies a port on the device (for Fibre
Channel only).