XYGATE Merged Audit Reference Manual
Table Of Contents
- Cover
- Copyright
- Publication History
- Contents
- Quick Reference for Common Tasks
- Introduction
- 1. Installing XMA
- 1.1 Before You Begin
- 1.2 Installing XMA Using the Automated Install Script
- 1.3 Installing the SIEM Log Adapter
- 1.4 Upgrading XMA or XTR Using the AutoInstall Script
- 1.5 Upgrade Considerations
- 1.6 Uninstalling XMA or XTR Using the Auto Uninstall Script
- 1.7 Managing the XYGATE License
- 1.8 Generate Reports Using XYGATE Report Manager (XRM)
- 2. Sending Data to Your ArcSight SIEM
- 3. Configuring Filters and the FILTERS File
- 3.1 How to Edit the FILTERS File
- 3.2 Filter Syntax
- 3.3 Building a Filter
- 3.3.1 Step 1. Name the Filter
- 3.3.2 Step 2. Set the Filter Status
- 3.3.3 Step 3: Set the EVALUATE_MSG Keyword
- 3.3.4 Step 4. Define the Filter’s Mover
- 3.3.5 Step 5. Define the Filter’s Data Selection Criteria
- 3.3.6 Step 6. Define the Filter’s Action
- 3.3.7 Step 7. Syntax Check and Compile Your FILTERS File
- 3.3.8 Step 8. Test Your Alerts
- 3.4 Variable Substitution Processing in the FILTERS File
- 3.5 Node-Conditional Processing in the FILTERS File
- 3.6 Determine the TCP/IP Process for Email, IPALERT, SNMP Alerts
- 3.7 Sending XMA Data to an Audit Logging Appliance
- 4. Generating Reports Using XRM
- 4.1 Generating Audit Reports Using XMA_REPORT
- 4.2 Select the Audit Subvolume
- 4.3 Select by Date and/or Time Range
- 4.4 Select by Subject Userid
- 4.5 Select by Subject Login Name(s)
- 4.6 Select by System
- 4.7 Select by Subject Terminal
- 4.8 Select Subject by Object Type
- 4.9 Select by Object Name
- 4.10 Select by Operation
- 4.11 Select By Outcome
- 4.12 Select the Output File’s Location
- 4.13 Select the Report’s Sort Order
- 4.14 Select by Rule Name
- 4.15 Select by XYGATE Product Code
- 4.16 Select by ALERTED Column
- 4.17 Select by Text in the Result Column
- 4.18 Select by Message Code
- 4.19 Select by Message ID
- 4.20 Run the Report
- 4.21 Running Reports from Archived Tables
- 5. Using XMA_MANAGER
- 6. Configuring MOVERs
- 7. Safeguard Selection Criteria
- 8. Maintaining the XMA Database
- 9. Troubleshooting
- A: The MACONF File
- B: Administrative Tables
- B1: XYGATE MOVER Configuration Tables
- B2: XYGATE MOVER State Tables
- B3: EMS MOVER Table =XMA__EMSMVTBL
- B4: EMS MOVER Parameters Table =XMA_EMSMVPARAMSTBL
- B5: EMS MOVER State Table =XMA_EMSMVSTATETBL
- B6: MEASURE MOVER Tables
- B7: SAFEGUARD MOVER Table =XMA_SFGMVTBL
- B8: SAFEGUARD Parameter Table =XMA_SFGMVPARAMSTBL
- B9: SAFEGUARD MOVER State Tables
- B10: BASE24 MOVER Table
- B11: BASE24 Parameter Table
- B12: BASE24 State Tables
- B13: TCP/IP Syslog Tables
- B14: HLR MOVER TABLE
- B15: HLR Parameter Table
- B16: HLR State Tables
- B17: iTP Secure WebServer MOVER Table
- B18: iTP Secure WebServer State Table
- B19: ARCHIVE Tables
- B20: PARAMS Table
- B21: SESSIONOIP Table
- C: Data Tables
- D: Sample Filters
- D1: Filter out $CMON’s “I’m Alive” Messages
- D2: Filter out XPC STATUS Commands
- D3: Filter out Safeguard reading its own user database
- D4: Filter out Safeguard No Record
- D5: Filter out XOS No Record
- D6: Filter out XOS What-if tests
- D7: Alert for SUPER.SUPER’s password change via XPQ
- D8: Alert when someone logs directly on as SUPER.SUPER
- D9: Alert for XAC command containing "–255"
- D10: Selecting security-related BASE24 EMS events
- D11: Selecting CLIM events
- E: XMA Host Macros
- E1: ADELMAC
- E2: ARCMAC
- E3: CLEANDB
- E4: EMSBUILD
- E5: PARSAMP
- E6: REMFIN
- E7: UPDSTAT
- E8: XMA_AUDIT_REPORT
- E9: XMA_COMPILE_FILTERS
- E10: XMA_DATETIME_MAKE
- E11: XMA_DBVOLUME
- E12: XMA_EDIT_FILTERS
- E13: XMA_FILTERS_CHECK
- E14: XMA_INSTALL_LICENSE
- E15: XMA_LOAD_DEFINES
- E16: XMA_NETWORK_FILTERS_CHECK
- E17: XMA_NETWORK_LICENSE_INSTALL
- E18: XMA_NETWORK_VERSION
- E19: XMA_PWCOLD
- E20: XMA_PWCOOL
- E21: XMA_PWSTOP
- E22: XMA_PWVOLUME
- E23: XMA_SQLCOMPALL
- E24: XMA_SYNTAX_CHECK
- E25: XMA_UPDATE_FILTERS
- E26: XMA_VERSION
- E27: XMA_VOLUME
- F: TCLEXC
- G: Data Mapping
- G1: General Notes on Data Mapping Columns
- G2: Column Descriptions
- G3: How to Use the Data Mapping Tables
- G4: BASE24 Data Mapping
- G5: BASE24-eps Data Mapping
- G6: HLR Data Mapping
- G7: EMS Data Mapping
- G8: iTP Secure WebServer Mapping
- G9: Measure Data Mapping
- G11: Safeguard Data Mapping
- G12: XYGATE Access Control (XAC) Data Mapping
- G13: XYGATE Supported CMON (XCM) Data Mapping
- G14: XYGATE Host Encryption (XHE) Data Mapping
- G15: XYGATE Key Management (XKM) Data Mapping
- G16: XYGATE Process Control (XPC) Data Mapping
- G17: XYGATE Password Quality (XPQ) Data Mapping
- G18: XYGATE Object Security (XOS) Data Mapping
- G19: XYGATE Safeguard Manager (XSM) Data Mapping
- G20: XYGATE Combined Spoolcom Peruse Data Mapping (XSP)
- G21: XYGATE Transaction Router (XTR) Data Mapping
- G22: XYGATE User Authentication (XUA) Data Mapping
- G23: XYGATE Compliance PRO (XSW) Data Mapping
- G24: Column Usage Table
- Glossary
- Index
XYGATE Merged Audit
®
Reference Manual
Chapter 3. Configuring Filters and the FILTERS File
XYPRO Technology Corporation 68 Proprietary and Confidential
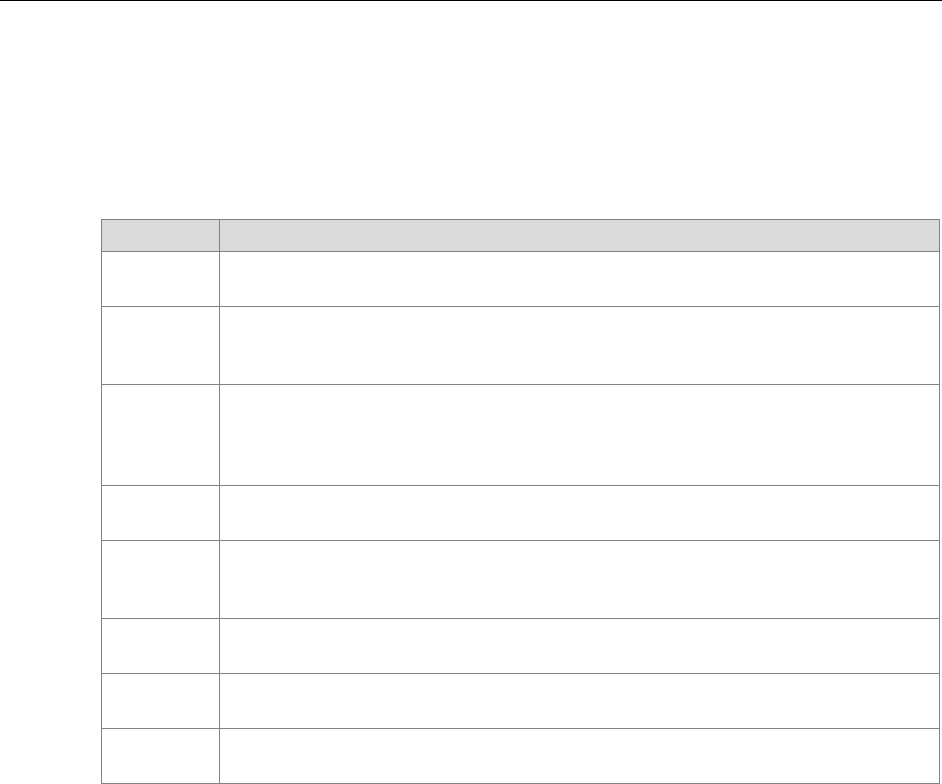
Tracking Your Alerts
For reporting purposes, there is a column called ALERTED in the Audit Detail Table
This column contains a one-character flag to indicate the alert status.
The ALERTED Column will contain one of the following values:
Value Description
A
Alert – The alert was issued.
B
Blocked - The record was eligible for an ALERT but the parameter
BLOCKALERTS was set to TRUE (refer to section 6.9, “MOVER Parameters”
on page 129 for more information).
C
Collect-Only – In an Alert Only/Collect-Only environment, the Collectors
update the database with a C if an event would have generated an alert, but
the actual alert would have been generated by the Alert only MOVER, which
does no update the database.
D
Duplicate – The record was eligible for issue but the time specified in
MAXACTIONRATE has not passed.
F
Failed – The attempt failed. This indicates that a problem has occurred and
the desired ACTION cannot be performed before the MAXCOMPLETIONTIME
has been reached.
G
GLOBALBLOCKALERTS is set to ON. An ALERT would have been issued,
but all ALERTS where being suppressed.
N
Not Eligible (default).
O
Old – The record was eligible for issue but older than the value specified in
MAXRECORDAGE.
Note: MAXRECORDAGE, MAXACTIONRATE allow you to control the number of
ALERTS and ACTIONs that occur. A description of these parameters can be
found Chapter 3 under the heading “Step 6. Define the Filter’s Action” on
page 54.
3.3.7 Step 7. Syntax Check and Compile Your FILTERS File
It is recommended, for back out purposes, that changes be made to a copy of the
FILTERS file and the new version moved in after a successful syntax check. The
macros XMA_EDIT_FILTERS and XMA_UPDATE_FILTERS described in Appendix E:
“XMA Host Macros” starting on page 203 are available to facilitate this process. Both
of these macros will also create or update MACONFB, the compiled version of the
FILTERS file.
If you have a multi-node installation, both XMA_EDIT_FILTERS and
XMA_UPDATE_FILTERS macros will compile and update the MACONFB file on all
nodes. A copy of MACONFB is being place on each node to accommodate node
conditional processing.










