HP XP7 RAID Manager Installation and Configuration User Guide (T1610-96065)
Table Of Contents
- XP7 RAID Manager Installation and Configuration User Guide
- Contents
- 1 Installation requirements
- System requirements
- Supported environments
- Supported Business Copy environments
- Supported Continuous Access Synchronous environments
- Supported Continuous Access Asynchronous environments
- Supported Continuous Access Journal environments
- Supported Snapshot environments
- Supported Data Retention environments
- Supported Database Validator environments
- Supported guest OS for VM
- Supported IPv4, IPv6 platforms
- Requirements and restrictions for z/Linux
- Requirements and restrictions for VM
- Porting notice for OpenVMS
- Using RAID Manager with Hitachi and other storage systems
- 2 Installing and configuring RAID Manager
- 3 Upgrading RAID Manager
- 4 Removing RAID Manager
- 5 Troubleshooting
- 6 Support and other resources
- A Fibre-to-SCSI address conversion
- B Sample configuration definition files
- Glossary
- Index
Fibre address conversion tables
Table 15 (page 55), Table 16 (page 55), Table 17 (page 56) and show the fibre address conversion
tables:
• Table number 0 = HP-UX systems (see Table 15 (page 55))
• Table number 1 = Solaris and IRIX systems (see Table 16 (page 55))
• Table number 2 = Windows systems (see Table 17 (page 56))
The conversion table for Windows systems is based on the Emulex driver. If a different fibre-channel
adapter is used, the target ID indicated by the raidscan command may be different than the target
ID indicated by the Windows system.
Note on Table 3 for other Platforms: Table 3 is used to indicate the LUN without Target ID for
unknown FC_AL conversion table or fibre-channel fabric (fibre-channel world wide name). In this
case, the Target ID is always zero, thus Table 3 is not described in this document. Table 3 is used
as the default for platforms other than those listed above. If the host will use the WWN notation
for the device files, then this table number should be changed by using the $HORCMFCTBL variable.
If the TID displayed on the system is different than the TID indicated in the fibre address conversion
table, you must use the TID (or LU#) returned by the raidscan command to specify the device(s).
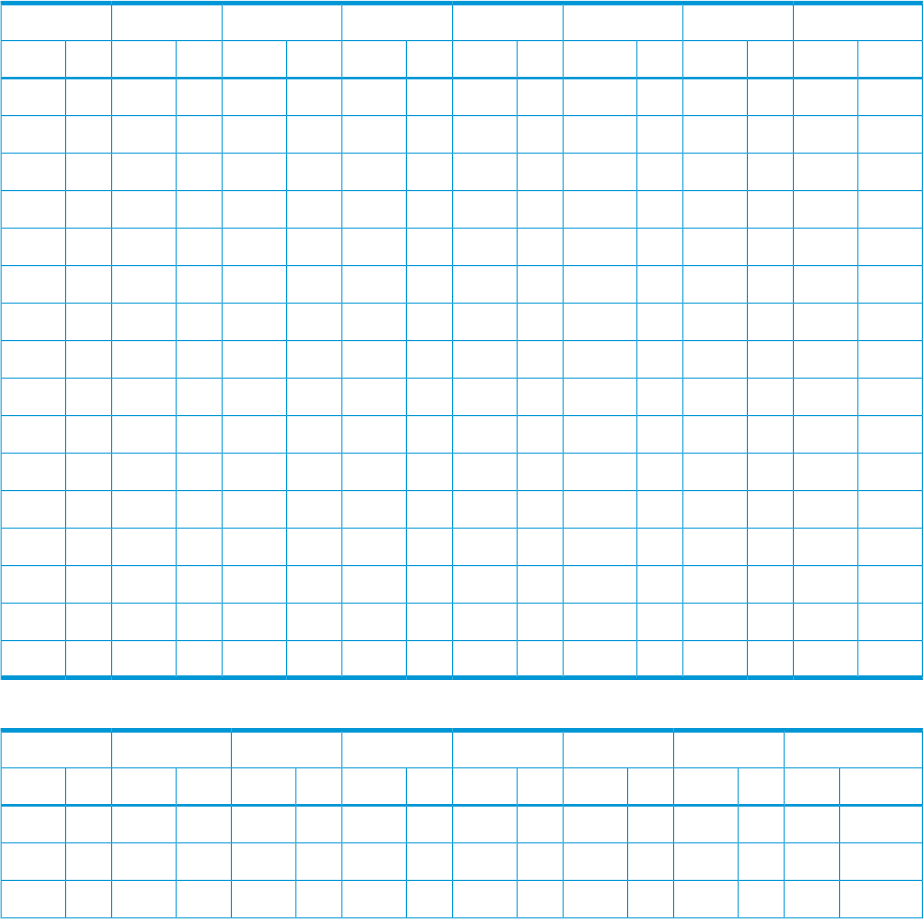
Table 15 Fibre Address Conversion Table for HP-UX Systems (Table0)
C7C6C5C4C3C2C1C0
TIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PA
02503A0550720980B20CD0EF
1231391541711971B11CC1E8
21F23625326E2902AE2CB2E4
31E33535236D38F3AD3CA3E2
41D43445146C4884AC4C94E1
51B53354E56B5845AB5C75E0
61863264D66A6826AA6C66DC
71773174C7697817A97C57DA
81082E84B8678808A78C38D9
90F92D94A96697C9A69BC9D6
1008102C10491065107A10A510BA10D5
1104112B11471163117911A311B911D4
1202122A1246125C1276129F12B612D3
130113291345135A1375139E13B513D2
--1427144314591474149D14B414D1
--1526153C15561573159B15B315CE
Table 16 Fibre Address Conversion Table for Solaris and IRIX Systems (Table1)
C7C6C5C4C3C2C1C0
TIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PATIDAL-PA
11225963A80556472489832B216CD0EF
11323973981546571499733B117CC1E8
1141F98368253666E509034AE18CB2E4
Fibre address conversion tables 55










