HP XP7 RAID Manager Installation and Configuration User Guide (T1610-96065)
Table Of Contents
- XP7 RAID Manager Installation and Configuration User Guide
- Contents
- 1 Installation requirements
- System requirements
- Supported environments
- Supported Business Copy environments
- Supported Continuous Access Synchronous environments
- Supported Continuous Access Asynchronous environments
- Supported Continuous Access Journal environments
- Supported Snapshot environments
- Supported Data Retention environments
- Supported Database Validator environments
- Supported guest OS for VM
- Supported IPv4, IPv6 platforms
- Requirements and restrictions for z/Linux
- Requirements and restrictions for VM
- Porting notice for OpenVMS
- Using RAID Manager with Hitachi and other storage systems
- 2 Installing and configuring RAID Manager
- 3 Upgrading RAID Manager
- 4 Removing RAID Manager
- 5 Troubleshooting
- 6 Support and other resources
- A Fibre-to-SCSI address conversion
- B Sample configuration definition files
- Glossary
- Index
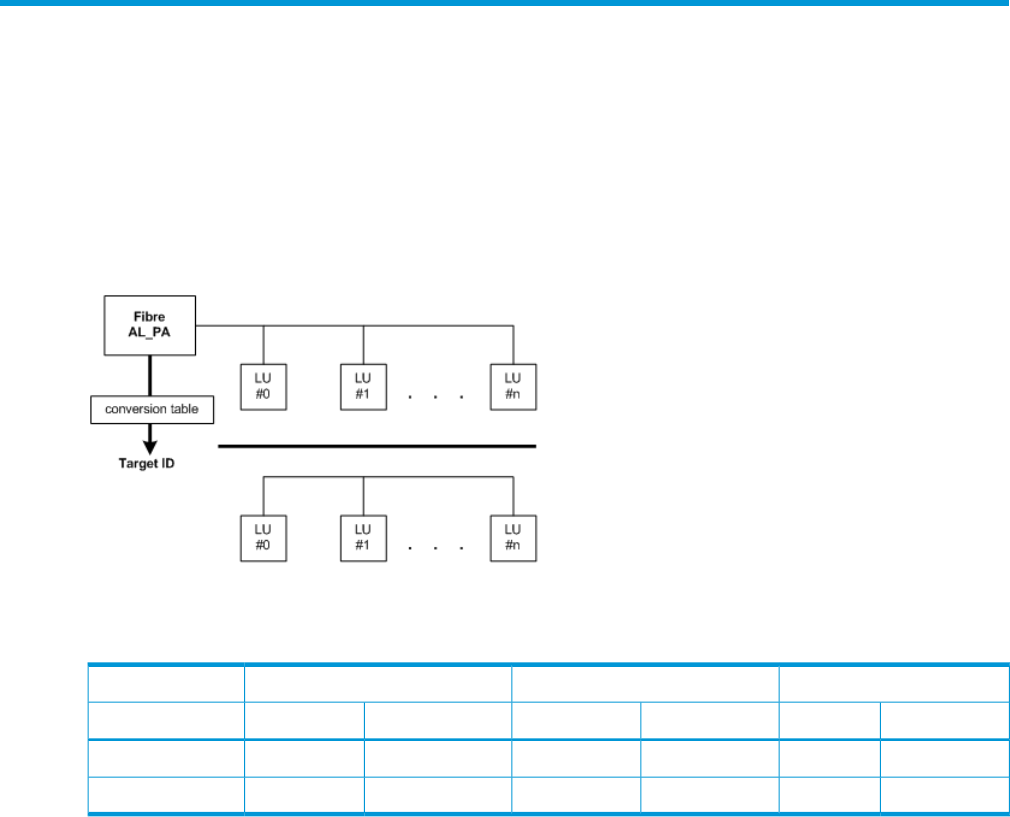
A Fibre-to-SCSI address conversion
Disks connected with fibre channel display as SCSI disks on UNIX hosts. Disks connected with
fibre channel connections can be fully utilized. RAID Manager converts fibre-channel physical
addresses to SCSI target IDs (TIDs) using a conversion table (see Figure 9 (page 52)).
Table 14 (page 52) shows the current limits for SCSI TIDs and LUNs on various operating systems.
Fibre/FCoE-to-SCSI address conversion
Figure 9 Example Fibre Address Conversion
If ISCSI, AL_PA is fixed a value 0xFE.
Table 14 Limits for Target IDs and LUNs
Windows SystemsSolaris, IRIX SystemsHP-UX, other Systems-
LUNTIDLUNTIDLUNTIDPort
0 to 10230 to 310 to 10230 to 1250 to 10230 to 15Fibre
0 to 70 to 150 to 70 to 150 to 70 to 15SCSI
Conversion table for Windows. The conversion table for Windows is based on conversion by an
Emulex driver. If the fibre-channel adapter is different (for example, Qlogic, HP), the target ID that
is indicated by the raidscan command may be different from the target ID on the Windows host.
Example 6 “Using Raidscan to Display TID and LUN for Fibre-Channel Devices” shows an example
of using the raidscan command to display the TID and LUN of Harddisk6 (HP driver). You must
start HORCM without the descriptions of HORCM_DEV or HORCM_INST in the configuration
definition file because of the unknown TIDs and LUNs.
52 Fibre-to-SCSI address conversion










