Performance and Recommended Use of AD222A, AD393A, and AD221A PCIe Combination 4-Gbit/s Fibre Channel and Gigabit Ethernet Cards
8
Request-Response tests were also run to demonstrate the capability of how the adapter
handles traffic of this nature. TCP Request-Responses tests were run using a request size of
1-byte and a response size of 1-byte. The aggregate number of transactions that could be
sustained with a processor per port running close to saturation was captured. Figure 7
below shows the number of transactions per second.
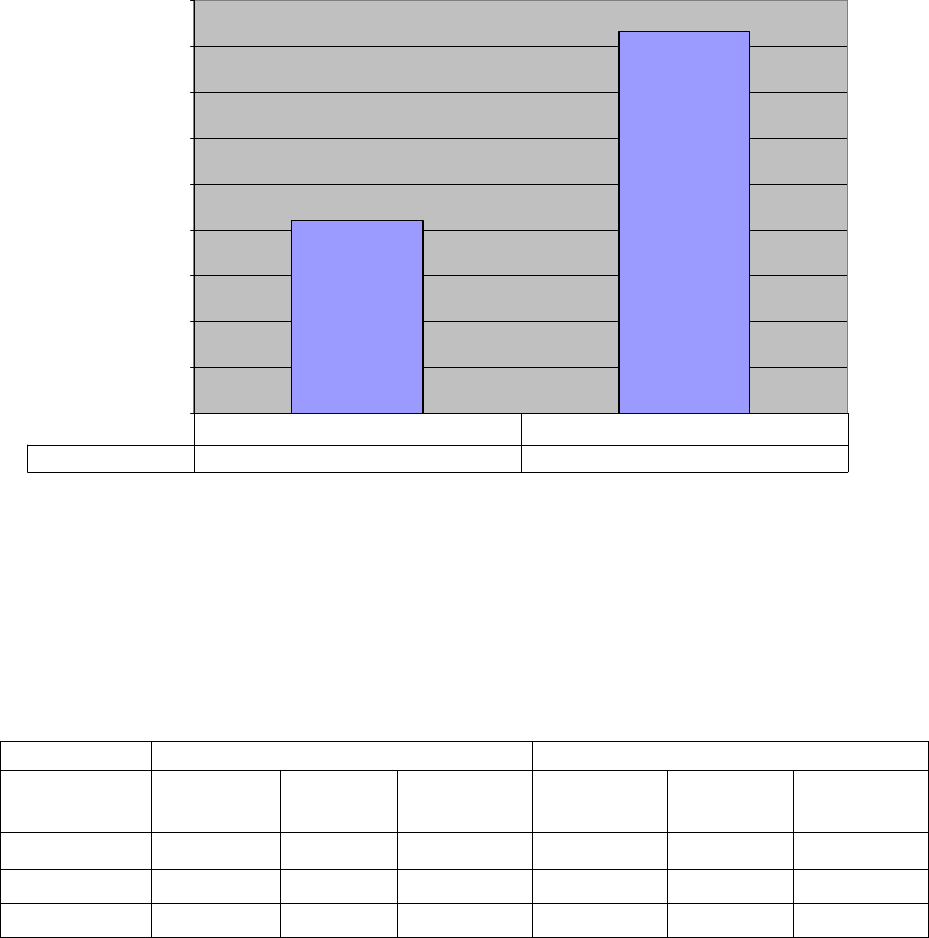
Figure 7: AD222A Gigabit Ethernet Request Response Transactions
0
20000
40000
60000
80000
100000
120000
140000
160000
180000
Transactions Per Second
Transcations Per Second
83966 166302
1 Port 2 Ports
Service demand and CPU Utilization are also measured for each throughput test. Table 2
shows the details. Service demand is the amount of time (in microseconds) it takes a CPU
to handle one kilobyte of data. It is a normalized measurement because it eliminates
disparities due to differences in quantities, types, or frequencies of CPUs. CPU utilization
is normalized over 8 CPUs.
Table 2 Gigabit Ethernet Service Demand
1 Gigabit Ethernet Port 2 Gigabit Ethernet Ports
1500-byte
MTUs
Throughput
mbit/s
SD
usec/KB
CPU
Utilization
Throughput
mbit/s
SD
usec/KB
CPU
Utilization
Transmit 948 2.098 3% 1,895 2.077 6%
Receive 948 3.333 5% 1,895 3.368 10%
Bi-directional 1,880 2.959 8% 3,762 3.017 17%










