HP ProCurve Switch / Wireless - Using 802.11e and WMM on the ProCurve Wireless Edge Services Module
Using 802.11e and WMM on the ProCurve Wireless Edge Services Module
HP ProCurve Networking
7
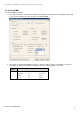
3.5 General configuration tips
• Low AIFSN and low CWmin will provide low latency, high throughput.
• By default, high-priority queues on the radio port use AIFSN=1ms; high-priority queues on stations use
AIFSN= 2ms.
• If Transmit Ops is too high, a station can use the medium for a long time and other traffic may be delayed.
Generally Transmit Ops is best set to a maximum of 100ms.
• Increasing CWmax can decrease the number of collisions.
• CWmax must always be higher than CWmin.
4. WMM implementation by telephony vendors
WMM is a popular standard, and has been adopted by most wireless IP telephone vendors, including Cisco, Aastra,
Alcatel, Avaya, Siemens, and Spectralink-Polycom.
5. U-APSD
U-APSD (Unscheduled Automatic Power Save Delivery) has been adopted by the WiFi Alliance, where it is known as
WMM Power Save. This technology allows saving battery power and fine-tuning the power consumption of wireless
stations on WMM-enabled wireless networks. WMM Power Save Certification is a part of the WMM certification as
defined by the WiFi Alliance.
With U-APSD, data destined to a wireless station such as a PDA or phone can be transmitted in a shorter time period,
while allowing the device to stay longer in a low-power sleep mode. When the device wakes up, the client sends a
trigger frame to the access point to obtain the data. The application, not the device driver, decides when the client will
communicate with the access point, allowing more granularity in adapting the power save mechanism to the
application use (e.g., to voice traffic).
To take advantage of U-APSD, both the AP and the client must have WMM enabled. U-APSD can coexist with legacy
devices and networks. Improvements in battery life range from 15 percent to 40 percent.