HP ProCurve Threat Management Solution Design Guide 2009-04
4-10
Design
Background for Planning NIM Policies
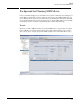
If you look at the general policy flow diagram in Figure 4-3, you will see where many of those
events occur.
Figure 4-3. General Policy Flow
Consider first the NBAD engine. It analyzes traffic metrics (sFlow and XRMON samples) from
PCM+ to find anomalous behaviors that indicate network threats. These detected threats show
up as NBAD events in the Events window.
To help you understand NBAD events, NIM includes the NBAD Diagnostic Wizard. You can run
the wizard to analyze a particular NBAD event. It will help you identify the possible cause and
determine possible solutions.
In addition to NBAD events, NIM can receive Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
traps from:
■ HP ProCurve wired devices
■ HP ProCurve wireless devices
■ HP ProCurve security devices
■ Third-party security devices
(Currently, there is one ProCurve security device: the TMS zl Module.)
The ProCurve switches that support Virus Throttle
TM
technology (connection-rate filtering)
can send these SNMP traps to NIM. Some ProCurve switches also include security features
such as those listed below and can send NIM SNMP traps when they detect suspicious activity
or traffic:
■ Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping
■ Dynamic Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) protection
■ Instrumentation monitor
■ SNMP authentication failures
■ Command-line interface (CLI) password authentication failures
■ Authentication server failures
■ Port security authentication failures
NIM receives these SNMP traps and shows them as events in the PCM+ Events window.
NBAD engine
Policies Section
Alerts Section Actions Section
Policies
Alerts Actions
Policy Configuration Manager Panel
sFlow and
XRMON
Data
Virus
Throttling
Events
IDS, IPS
Events
Security
Monitoring
Panel
Define
Actions
Define
Alerts
Define
Policies
Set
Sensitivities
NBAD
Events
External
Events
ProCurve
Events