HP TMS zl Module Security Administrator's Guide
4-338
Configuring a VPN on the HP TMS zl Module
GRE Tunnels
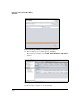
Table 4-38 lists the necessary access policies; the numbers in the Source and
Destination columns refer to the example figure above. (Note that all of these
policies are typically configured for the None User group. However, if local
users log in through the module, then the access policies with the local zone
as the source zone would use that user group.)
For access policies that permit the traffic sent over the tunnel, you should
consider setting the TCP MSS to a value lower than the typical MSS used in
your system. Otherwise, the addition of the GRE and IP delivery headers might
make the packets too large to be transmitted. Table 4-38 suggests a value for
the TCP MSS when the MTU is 1500. For more information on the TCP MSS,
see “Maximum Segment Size (MSS) for TCP Connections” on page 4-26.
Note The value for TCP MSS in the table is only a suggestion. You should determine
the best setting for your environment.
Table 4-38. Checklist for Access Policies for a GRE Tunnel
When Required Ty pe From Zone To Zone Service Source Destination MSS Number of
policies
Always Unicast Remote SELF (47) GRE 3 1 — 1
Always Unicast SELF Remote (47) GRE 1 3 — 1
Always Unicast Local Tunnel Any that you
choose
2 4 1436 As many as
you choose
Always Unicast Tunnel Local Any that you
choose
4 2 1436 As many as
you choose
Tunnel must carry
multicasts
Multicast Local Tunnel Any that you
choose
2 Any Address
or multicast
address
— As many as
you choose
Tunnel must carry
multicasts
Multicast Tunnel Local Any that you
choose
4 Any Address
or multicast
address
— As many as
you choose
• Dynamic
routing over
the tunnel
• Default
policies
disabled
Unicast Tunnel SELF OSPF or RIP 6 5 1436 1
• Dynamic
routing over
the tunnel
• Default
policies
disabled
Unicast SELF Tunnel OSPF or RIP 5 6 1436 1