HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
104
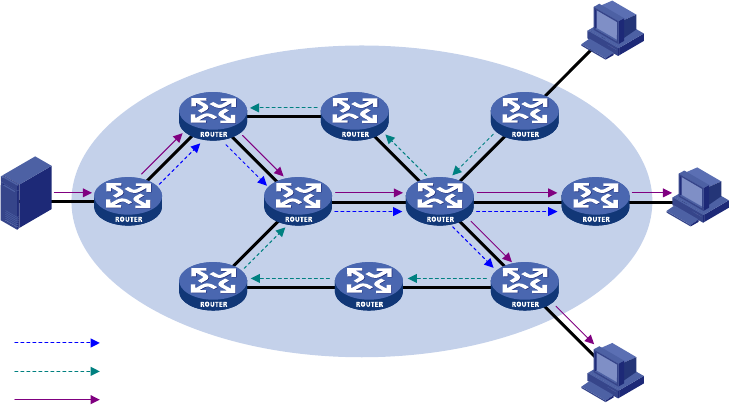
Figure 67 SPT establishment in an IPv6 PIM-DM domain
The flood-and-prune process takes place periodically. A pruned state timeout mechanism is provided. A
pruned branch restarts multicast forwarding when the pruned state times out. It is pruned again when it
no longer has any multicast receiver.
Graft
When a host attached to a pruned node joins an IPv6 multicast group, to reduce the join latency, IPv6
PIM-DM uses the graft mechanism to resume IPv6 multicast data forwarding to that branch. The process
is as follows:
1. The node that needs to receive IPv6 multicast data sends a graft message to its upstream node,
requesting to join the SPT again.
2. After receiving this graft message, the upstream node puts the interface that received the graft
message into the forwarding state and responds with a graft-ack message to the graft sender.
3. If the node that sent a graft message does not receive a graft-ack message from its upstream node,
it keeps sending graft messages at a configurable interval until it receives an acknowledgment
from its upstream node.
Assert
On a shared-media network with more than one multicast router, the assert mechanism shuts off duplicate
IPv6 multicast flows to the network. It does this by electing a unique IPv6 multicast forwarder for the
shared-media network.
Source
Server
Host A
Host B
Host C
Receiver
Receiver
IPv6 multicast packets
SPT
Prune message










