HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
8
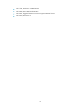
RIP message format
A RIP message consists of a header and up to 25 route entries. (A RIPv2 authentication message uses the
first route entry as the authentication entry, so it has up to 24 route entries.)
RIPv1 message format
Figure 1 RIPv1 message format
• Command—Type of message. 1 indicates a request, which is used to request all or part of the
routing information from the neighbor, and 2 indicates a response, which contains all or part of the
routing information. A response message consists of up to 25 route entries.
• Version—Version of RIP, 0x01 for RIPv1.
• Must be zero—This field must be zero.
• AFI—Address Family Identifier, 2 for IP.
• IP address—Destination IP address of the route. It can be a natural network, subnet or a host
address.
• Metric—Cost of the route.
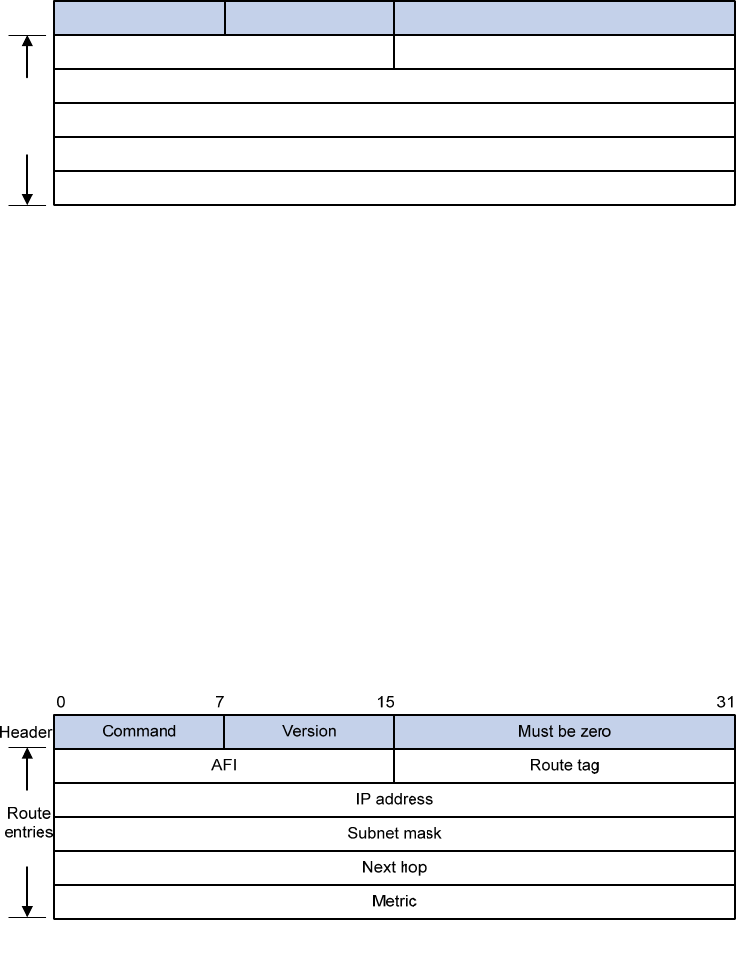
RIPv2 message format
The format of RIPv2 message is similar to RIPv1.
Figure 2 RIPv2 message format
The differences from RIPv1 are stated as follows:
• Version—Version of RIP. For RIPv2 the value is 0x02.
• Route tag—Route tag.
Command
AFI
IP address
Version Must be zero
Must be zero
Must be zero
Must be zero
Metric
0 7 15 31
Route
entries
Header