HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
9
• IP address—Destination IP address. It can be a natural network address, subnet address or host
address.
• Subnet mask—Mask of the destination address.
• Next hop—If set to 0.0.0.0, it indicates that the originator of the route is the best next hop;
otherwise it indicates a next hop better than the originator of the route.
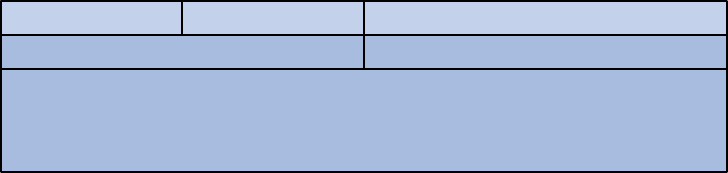
RIPv2 authentication message format
RIPv2 sets the AFI field of the first route entry to 0xFFFF to identify authentication information.
Figure 3 RIPv2 authentication message
• Authentication type—A value of 2 represents plain text authentication, while a value of 3
represents MD5.
• Authentication—Authentication data, including password information when plain text
authentication is adopted or including key ID, MD5 authentication data length and sequence
number when MD5 authentication is adopted.
RFC 1723 only defines plain text authentication. For information about MD5 authentication, see RFC
2453.
Supported RIP features
RIP supports the following features:
• RIPv1 and RIPv2
• RIP for MPLS VPNs
• BFD
RIP periodically sends route update requests to neighbors. If no route update response for a route is
received within the specified interval, RIP considers the route unreachable. This mechanism cannot detect
link faults quickly. After BFD is configured for RIP, and BFD detects a broken link, RIP can quickly age out
the unreachable route, thus avoiding interference to other services.
Protocols and standards
• RFC 1058, Routing Information Protocol
• RFC 1723, RIP Version 2 - Carrying Additional Information
• RFC 1721, RIP Version 2 Protocol Analysis
• RFC 1722, RIP Version 2 Protocol Applicability Statement
Command
0xFFFF
Authentication (16 octets)
Version Unused
Authentication type
0715 31