HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
14
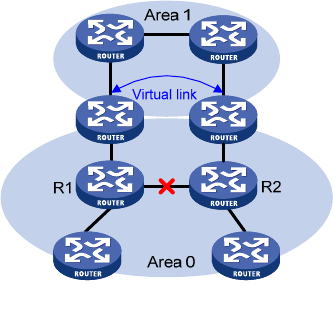
Figure 6 Virtual link application 2
The virtual link between the two ABRs acts as a point-to-point connection. You can configure interface
parameters, such as hello interval, on the virtual link as they are configured on a physical interface.
The two ABRs on the virtual link unicast OSPF packets to each other, and the OSPF routers in between
convey these OSPF packets as normal IP packets.
Stub area and totally stub area
A stub area does not distribute Type-5 LSAs to reduce the routing table size and the LSAs advertised
within the area. The ABR of the stub area advertises a default route in a Type-3 LSA so that the routers in
the area can reach external networks through the default route.
To further reduce the routing table size and advertised LSAs, you can configure the stub area as a totally
stub area. The ABR of a totally stub area does no advertise inter-area routes or external routes. It
advertises a default route in a Type-3 LSA so that the routers in the area can reach external networks
through the default route.
NSSA area and totally NSSA area
A NSSA area does not import AS external LSAs (Type-5 LSAs) but it can import Type-7 LSAs generated
by the NSSA ASBR. The NSSA ABR translates Type-7 LSAs into Type-5 LSAs and advertises the Type-5
LSAs to other areas.
You can configure an NSSA area as a totally NSSA area. The ABR of a totally NSSA area does no
advertise inter-area routes or external routes. It advertises a default route in a Type-3 LSA so that the
routers in the area can reach external networks through the default route.
In Figure 7, the O
SPF AS cont
ains Area 1, Area 2, and Area 0. The other two ASs run RIP. Area 1 is an
NSSA area where the ASBR redistributes RIP routes in Type-7 LSAs into Area 1. Upon receiving these
Type-7 LSAs, the NSSA ABR translates them to Type-5 LSAs, and advertises the Type-5 LSAs to Area 0.
The ASBR of Area 2 redistributes RIP routes in Type-5 LSAs into the OSPF routing domain. Area 1 cannot
receive these Type-5 LSAs because it is an NSSA area.










