HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
17
• On a NBMA network, OSPF packets are unicast, and neighbors are manually configured. On a
P2MP network, OSPF packets are multicast by default, and you can configure OSPF to unicast
protocol packets.
DR and BDR
On a broadcast or NBMA network, any two routers must establish an adjacency to exchange routing
information with each other. If n routers are present on the network, n(n-1)/2 adjacencies are established.
Any topology change on the network results in an increase in traffic for route synchronization, consuming
many system and bandwidth resources.
The DR and BDR mechanisms can solve this problem.
• DR—Elected to advertise routing information among other routers. If the DR fails, routers on the
network must elect another DR and synchronize information with the new DR. Using this mechanism
alone is time-consuming and prone to route calculation errors.
• BDR—Elected along with the DR to establish adjacencies with all other routers. When the DR fails,
the BDR immediately becomes the new DR, and other routers elect a new BDR.
Routers other than the DR and BDR are called "DROthers." They do not establish adjacencies with one
another, so the number of adjacencies is reduced.
The role of a router is subnet (or interface) specific. It might be a DR on one interface and a BDR or
DROther on another interface.
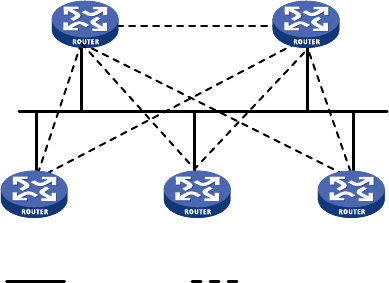
In Figure 9, soli
d lines are Ethernet physi
cal links, and dashed lines represent OSPF adjacencies. With
the DR and BDR, only seven adjacencies are established.
Figure 9 DR and BDR in a network
In OSPF, "neighbor" and "adjacency" are different concepts. After startup, OSPF sends a hello packet
on each OSPF interface. A receiving router checks parameters in the packet. If the parameters match its
own, the receiving router considers the sending router an OSPF neighbor. Two OSPF neighbors establish
an adjacency relationship after they synchronize their LSDBs through exchange of DD packets and LSAs.
DR and BDR election
DR election is performed on broadcast or NBMA networks but not on P2P or P2MP networks.
Routers in a broadcast or NBMA network elect the DR and BDR by router priority and ID. Routers with a
router priority value higher than 0 are candidates for DR and BDR election.
DR BDR
DR other DR otherDR other
Physical links Adjacencies










