HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
24
The DIS creates and updates pseudonodes, as well as generates their LSPs, to describe all routers on the
network.
A pseudonode represents a virtual node on the broadcast network. It is not a real router. In IS-IS, it is
identified by the system ID of the DIS and a one-byte Circuit ID (a non-zero value).
Using pseudonodes can reduce the resources consumed by SPF and simplify network topology.
NOTE:
On an IS-IS broadcast networks, all routers establish adjacency relationships, but they synchronize their
LSDBs through the DIS.
IS-IS PDUs
PDU
IS-IS PDUs are encapsulated in link layer frames. An IS-IS PDU has two parts, the headers and the
variable length fields. The headers comprise the PDU common header and the PDU specific header. All
PDUs have the same PDU common header. The specific headers vary by PDU type.
Figure 14 PDU format
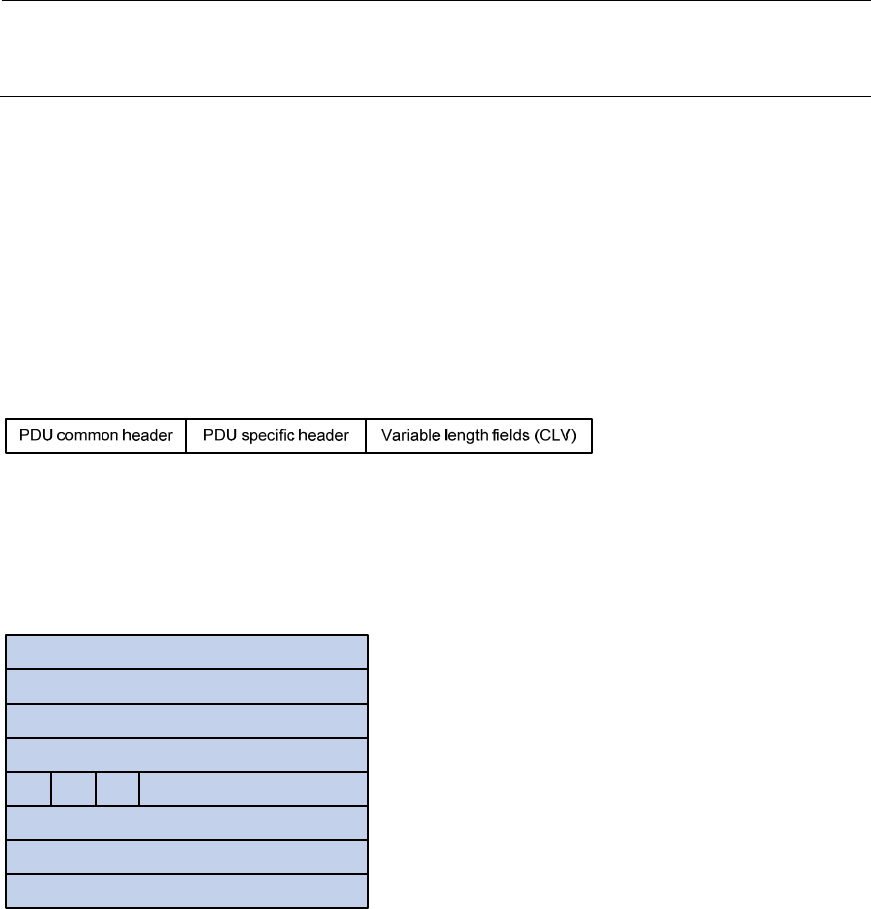
Common header format
Figure 15 PDU common header format
Major fields of the PDU common header are as follows:
• Intradomain routing protocol discriminator—Set to 0x83.
• Length indicator—Length of the PDU header in bytes, including both common and specific headers.
• Version/Protocol ID extension—Set to 1(0x01).
• ID length—Length of the NSAP address and NET ID.
• R(Reserved)—Set to 0.
• PDU type—For detailed information, see Table 4.
Intradomain routing protocol discriminator
Reserved
Version
R
ID length
Version/Protocol ID extension
Length indicator
Maximum area address
R R PDU type
No. of Octets
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1










