HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
25
• Version—Set to 1(0x01).
• Maximum area address—Maximum number of area addresses supported.
Table 4 PDU types
T
yp
e PDU T
yp
e Acron
y
m
15 Level-1 LAN IS-IS hello PDU L1 LAN IIH
16 Level-2 LAN IS-IS hello PDU L2 LAN IIH
17 Point-to-Point IS-IS hello PDU P2P IIH
18 Level-1 Link State PDU L1 LSP
20 Level-2 Link State PDU L2 LSP
24 Level-1 Complete Sequence Numbers PDU L1 CSNP
25 Level-2 Complete Sequence Numbers PDU L2 CSNP
26 Level-1 Partial Sequence Numbers PDU L1 PSNP
27 Level-2 Partial Sequence Numbers PDU L2 PSNP
Hello PDU
IS-to-IS hello PDUs (IIHs) are used by routers to establish and maintain neighbor relationships. On
broadcast networks, the Level-1 routers use the Level-1 LAN IIHs, and the Level-2 routers use the Level-2
LAN IIHs. The P2P IIHs are used on point-to-point networks.
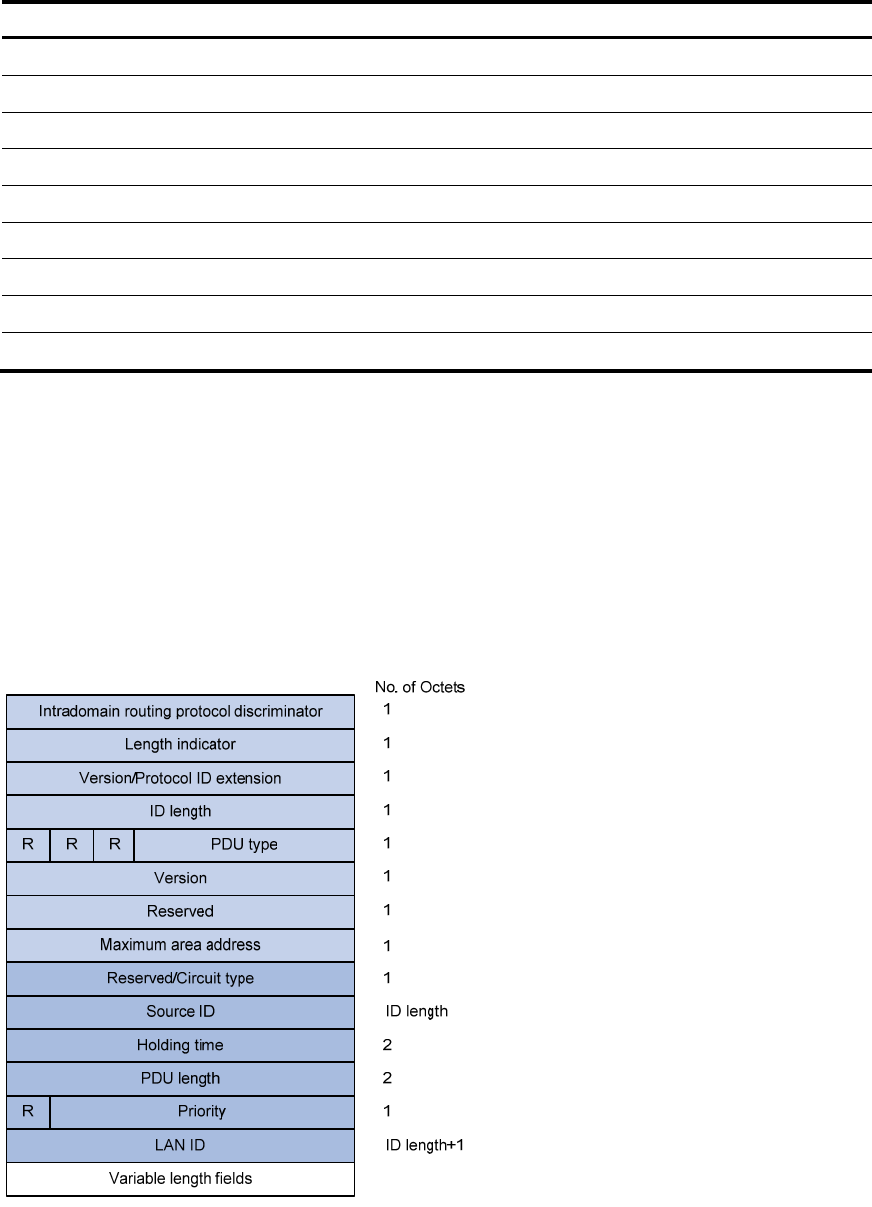
Figure 16 illu
strates the he
llo packet format in broadcast networks, where the blue fields are the common
header.
Figure 16 L1/L2 LAN IIH format










