HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
26
Major fields of the L1/L2 LAN IIH are as follows:
• Reserved/Circuit type—The first six bits are reserved with a value of 0. The last two bits indicate the
router type—00 means reserved, 01 indicates L1, 10 indicates L2, and 11 indicates L1/2.
• Source ID—System ID of the router advertising the hello packet.
• Holding time—If no hello packets are received from the neighbor within the holding time, the
neighbor is considered down.
• PDU length—Total length of the PDU in bytes.
• Priority—DIS priority.
• LAN ID—Includes the system ID and a one-byte pseudonode ID.
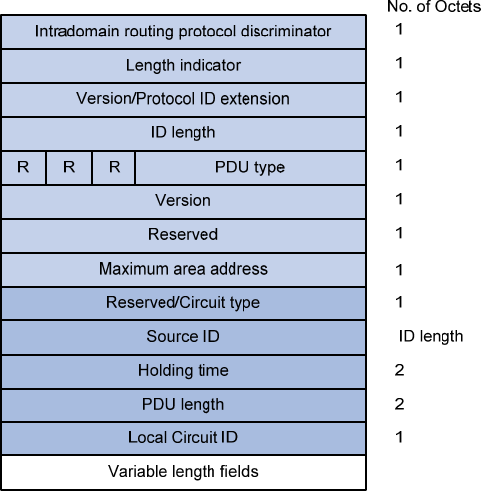
Figure 17 sho
ws the hello packet fo
rmat on the point-to-point networks.
Figure 17 P2P IIH format
Instead of the priority and LAN ID fields in the LAN IIH, the P2P IIH has a Local Circuit ID field.
LSP
The Link State PDUs (LSPs) carry link state information. LSPs include Level-1 LSPs and Level-2 LSP. The
Level-2 LSPs are sent by the Level-2 routers, and the Level-1 LSPs are sent by the Level-1 routers. The Level-1-2
router can send both types of LSPs.
The two types of LSPs have the same format, as shown in Figure 18.










