HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
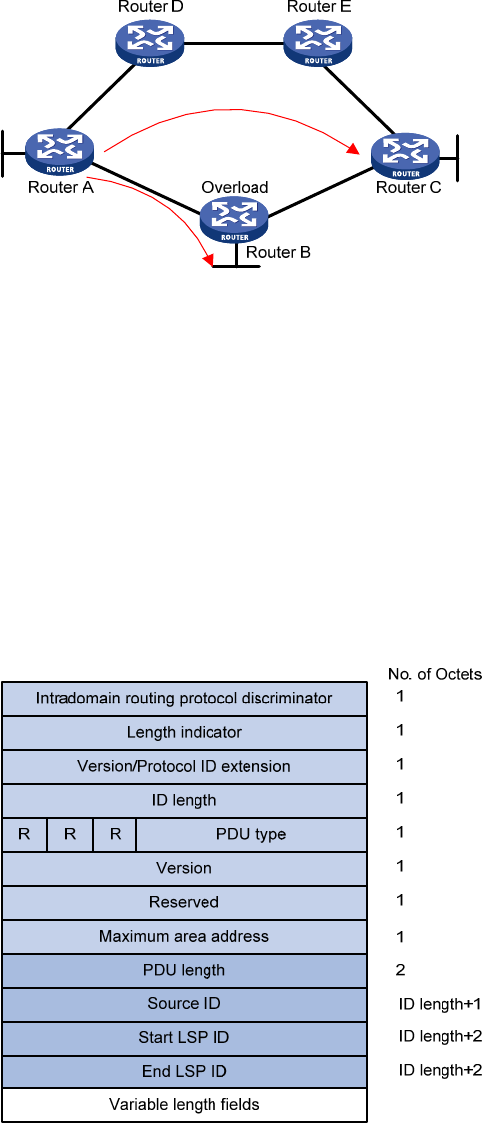
28
Figure 19 LSDB overload
SNP
A sequence number PDU (SNP) describes the complete or partial LSPs for LSDB synchronization.
SNPs include Complete SNP (CSNP) and Partial SNP (PSNP), which are further divided into Level-1 CSNP,
Level-2 CSNP, Level-1 PSNP and Level-2 PSNP.
A CSNP describes the summary of all LSPs for LSDB synchronization between neighboring routers. On
broadcast networks, CSNPs are sent by the DIS periodically (10 seconds by default). On point-to-point
networks, CSNPs are only sent during the adjacency establishment.
The CSNP packet format is shown in Figure 20.
Figure 20 L1/L
2 CSNP format
A PSNP only contains the sequence numbers of one or multiple latest received LSPs. It can acknowledge
multiple LSPs at one time. When LSDBs are not synchronized, a PSNP is used to request missing LSPs from
a neighbor.










