HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
34
• Notification—BGP sends a Notification message upon detecting an error and immediately closes
the connection.
BGP path attributes
BGP uses the following path attributes in update messages for route filtering and selection:
• ORIGIN
The ORIGIN attribute identifies the origin of routing information (how a route became a BGP route).
This attribute has the following types:
{ IGP—Has the highest priority. Routes generated in the local AS have the IGP attribute.
{ EGP—Has the second highest priority. Routes obtained through EGP have the EGP attribute.
{ INCOMPLETE—Has the lowest priority. The source of routes with this attribute is unknown. The
routes redistributed from other routing protocols have the INCOMPLETE attribute.
• AS_PATH
The AS_PATH attribute identifies the ASs through which a route has passed. Before advertising a
route to another AS, BGP adds the local AS number into the AS_PATH attribute, so the receiver can
determine ASs to route the message back.
The AS_PATH attribute has the following two types:
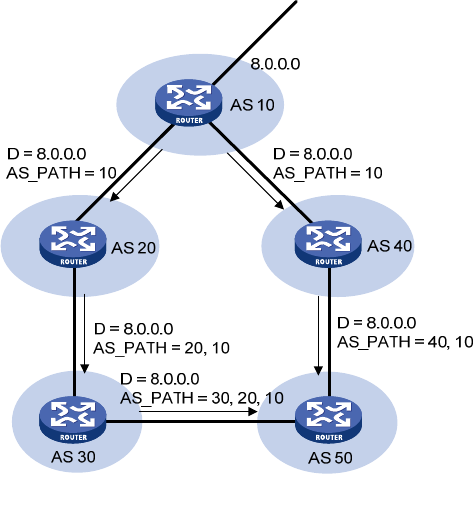
{ AS_SEQUENCE—Arranges AS numbers in sequence. As shown in Figure 23, the number of the
AS closest to the receiver's AS is the first one listed in the AS_PATH.
{ AS_SET—Arranges AS numbers randomly.
Figure 23 AS_PATH attribute
BGP uses the AS_PATH attribute to implement the following functions:
{ Avoid routing loops—A BGP router does not receive routes containing the local AS number to
avoid routing loops.










