HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
50
OSPFv3
The term "router" in this document refers to both routers and routing-capable firewalls and firewall
modules.
Overview
Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) supports IPv6 and complies with RFC 2740 (OSPF for IPv6).
OSPFv3 and OSPFv2 have the following similarities:
• A 32-bits router ID and area ID
• Packets, including Hello, Data Description (DD), Link State Request (LSR), Link State Update (LSU),
and Link State Acknowledgment (LSAck)
• Mechanism for finding neighbors and establishing adjacencies
• Mechanism for LSA flooding and aging
OSPFv3 and OSPFv2 have the following differences:
• OSPFv3 runs on a per-link basis, and OSPFv2 runs on a per-IP-subnet basis.
• OSPFv3 supports multiple instances per link, but OSPFv2 does not.
• OSPFv3 identifies neighbors by router ID, and OSPFv2 by IP address.
Packets
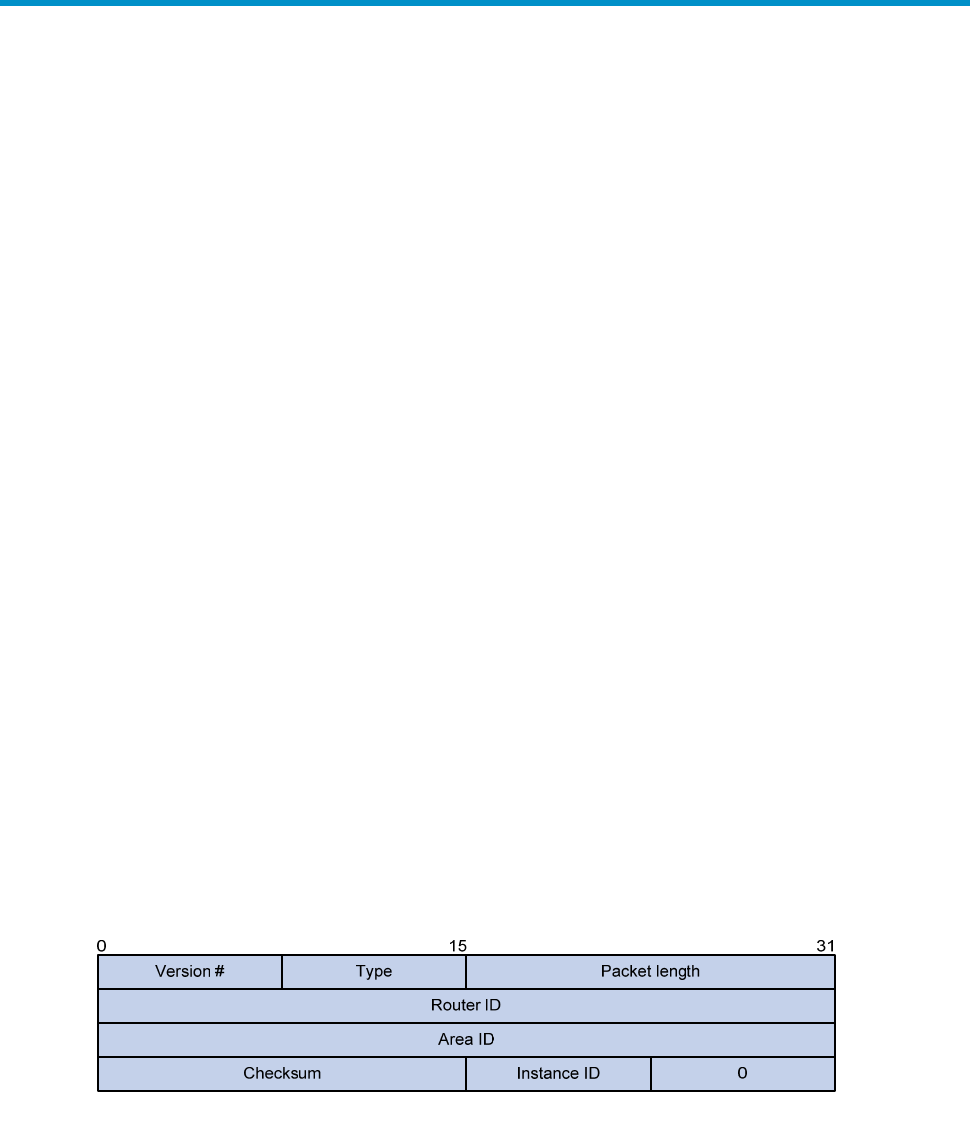
OSPFv3 has the following packet types: hello, DD, LSR, LSU, and LSAck. These packets have the same
packet header, which is different from the OSPFv2 packet header. The OSPFv3 packet header is only 16
bytes in length, and has no authentication field, but is added with an Instance ID field to support VPN per
link.
Figure 35 OSPFv3 packet header
Major fields for OSPFv3 packet header are as follows:
• Version #—Version of OSPF, which is 3 for OSPFv3.
• Type—Type of OSPF packet. Types 1 to 5 are hello, DD, LSR, LSU, and LSAck, respectively.
• Packet length—Packet length in bytes, including header.
• Instance ID—Instance ID for a link.
• 0—Reserved. It must be 0.










