HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
55
Multicast overview
Overview
As a technique that coexists with unicast and broadcast, the multicast technique effectively addresses the
issue of point-to-multipoint data transmission. By enabling high-efficiency point-to-multipoint data
transmission over a network, multicast greatly saves network bandwidth and reduces network load.
Using multicast technology, a network operator can easily provide new value-added services, such as
live webcasting, web TV, distance learning, telemedicine, web radio, real-time video conferencing, and
other bandwidth-critical and time-critical information services.
The term "router" in this document refers to both routers and routing-capable firewalls.
Unless otherwise stated, the term "multicast" in this document refers to IPv4 multicast.
Multicast overview
The information transmission techniques include unicast, broadcast, and multicast.
Unicast
In unicast transmission, the information source must send a separate copy of information to each host that
needs the information.
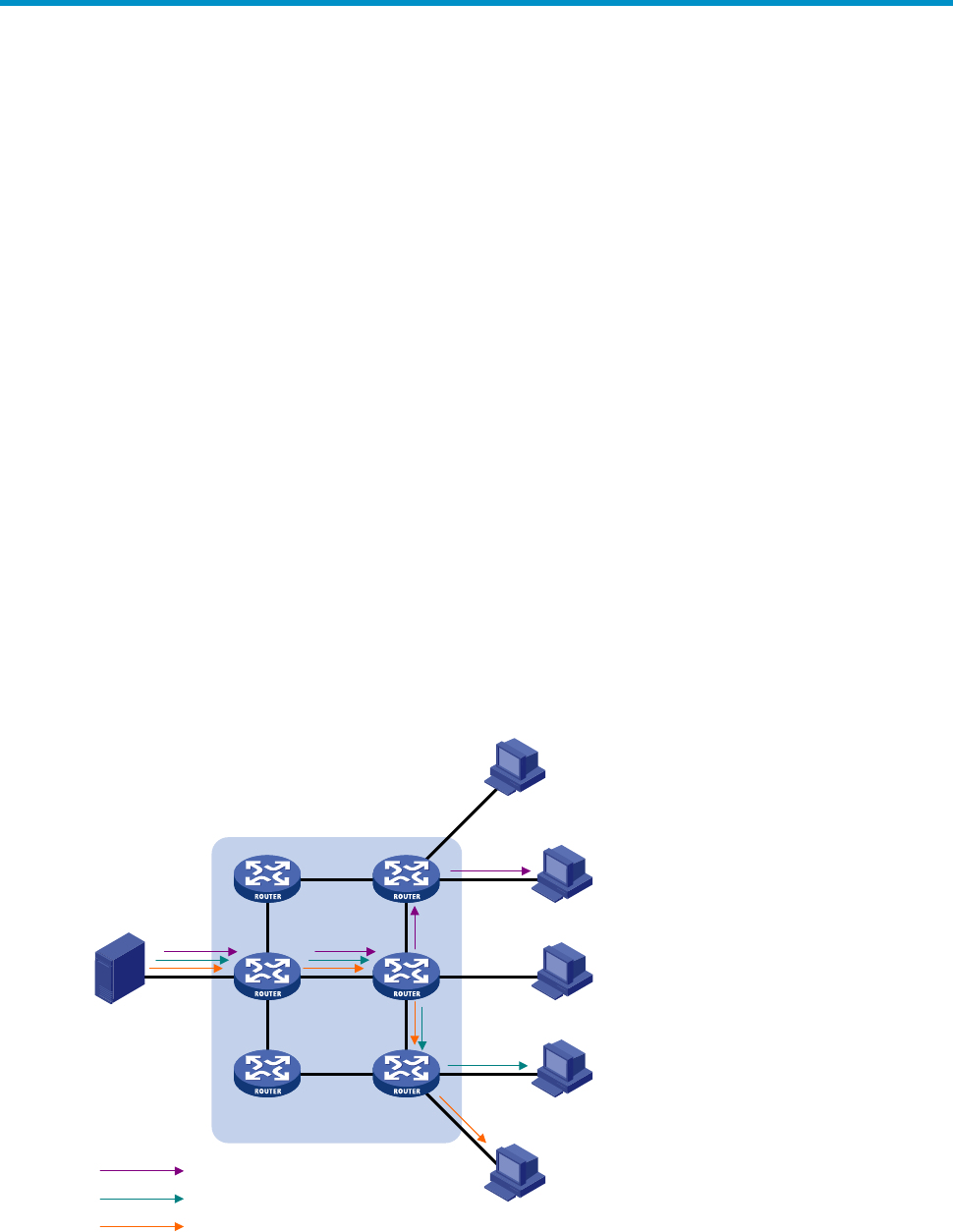
Figure 36 Unicast transmission
In Figure 36, assume that Host B, Host D and Host E need the information. A separate transmission
channel must be established from the information source to each of these hosts.
Source
Receiver
Receiver
Receiver
Host A
Host B
Host C
Host D
Host E
Packets for Host B
Packets for Host D
Packets for Host E
IP network










