HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
67
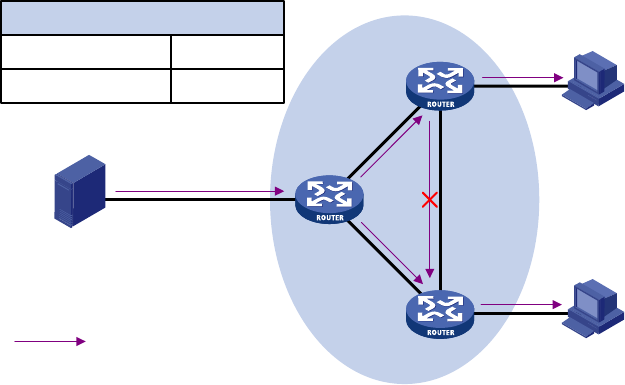
from the multicast source to the receivers. The multicast forwarding table on Router C contains the (S, G)
entry, with GigabitEthernet 0/1 as the incoming interface.
Figure 44 RPF check process
• When GigabitEthernet 0/1 of Router C receives a multicast packet, because the interface is the
incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing interfaces.
• When GigabitEthernet 0/2 of Router C receives a multicast packet, because the interface is not the
incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router performs an RPF check on the packet. The router
searches its unicast routing table and finds that the outgoing interface to Source (the RPF interface)
is GigabitEthernet 0/1 It means that the (S, G) entry is correct but the packet traveled along a
wrong path. The RPF check fails and the router discards the packet.
Static multicast routes
A static multicast route is an important basis for RPF check. It only affects RPF check but does not guide
multicast forwarding.
A static multicast route is effective only on the multicast router on which it is configured, and will not be
advertised throughout the network or redistributed to other routers.
Depending on the application environment, a static multicast route can change an RPF route and create
an RPF route.
Changing an RPF route
Typically, the topology structure of a multicast network is the same as that of a unicast network, and
multicast traffic follows the same transmission path as unicast traffic does. You can configure a static
multicast route for a given multicast source to change the RPF route, so that the router can create a
transmission path for multicast traffic that is different from the transmission path for unicast traffic.
Source
192.168.0.1/24
Receiver
Receiver
Router A
Router B
Router C
GE0/1
GE0/2
GE0/1
Multicast packets
Destination/Mask
IP Routing Table on Router C
192.168.0.0/24
Interface
GE0/1