HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
70
• Querier—The router that sends multicast traceroute requests is called the "querier."
Introduction to multicast traceroute packets
A multicast traceroute packet is a special IGMP packet that is different from common IGMP packets in
that its IGMP Type field is set to 0x1F or 0x1E and its destination IP address is a unicast address. The
following types of multicast traceroute packets are available:
• Query—Its IGMP Type field set to 0x1F.
• Request—Its IGMP Type field set to 0x1F.
• Response—Its IGMP Type field set to 0x1E.
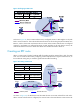
Process of multicast traceroute
1. The querier sends a query to the last-hop router.
2. After receiving the query, the last-hop router turns the query packet into a request packet by adding
a response data block to the end of the packet. The response data block contains its interface
addresses and packet statistics. The last-hop router then unicasts the request packet to the previous
hop for the given multicast source and group.
3. From the last-hop router to the multicast source, each hop adds a response data block to the end
of the request packet and unicasts it to the previous hop.
4. When the first-hop router receives the request packet, it changes the packet type to indicate a
response packet. Then, it sends the completed packet through unicast to the querier.