HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
77
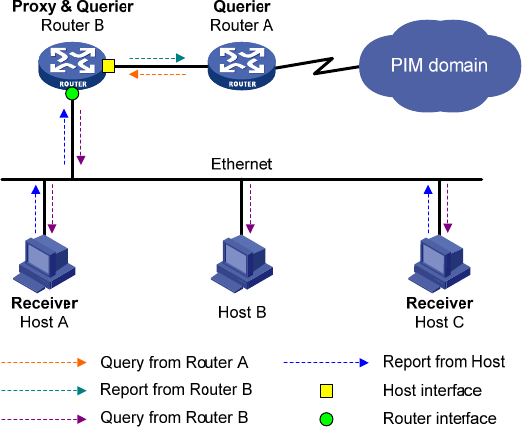
Figure 51 IGMP proxying
As shown in Figure 51, an IGMP proxy device has the following types of interfaces:
• Upstream interface—Also called the "proxy interface." A proxy interface is an interface on which
IGMP proxying is configured. It is in the direction toward the root of the multicast forwarding tree.
An upstream interface acts as a host that is running IGMP. Therefore, it is also called the "host
interface."
• Downstream interface—An interface that is running IGMP and is not in the direction toward the
root of the multicast forwarding tree. A downstream interface acts as a router that is running IGMP.
Therefore, it is also called the "router interface."
A device with IGMP proxying configured maintains a group membership database, which stores the
group memberships on all the downstream interfaces. Each entry comprises the multicast address, filter
mode, and source list. Such an entry is a collection of members in the same multicast group on each
downstream interface.
A proxy device performs host functions on the upstream interface based on the database. It responds to
queries according to the information in the database or sends join/leave messages when the database
changes. On the other hand, the proxy device performs router functions on the downstream interfaces by
participating in the querier election, sending queries, and maintaining memberships based on the
reports.
Protocols and standards
• RFC 1112, Host Extensions for IP Multicasting
• RFC 2236, Internet Group Management Protocol, Version 2
• RFC 3376, Internet Group Management Protocol, Version 3
• RFC 4605, Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)/Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD)-Based
Multicast Forwarding ("IGMP/MLD Proxying")










