HP VPN Firewall Appliances Appendix Protocol Reference
Table Of Contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- IP routing basics
- Static routing
- Default route
- RIP
- OSPF
- IS-IS
- BGP
- IPv6 static routing
- IPv6 default route
- RIPng
- OSPFv3
- IPv6 IS-IS
- IPv6 BGP
- Multicast overview
- Multicast routing and forwarding
- IGMP
- PIM
- MSDP
- IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding
- IPv6 PIM
- MLD
- Support and other resources
- Index
81
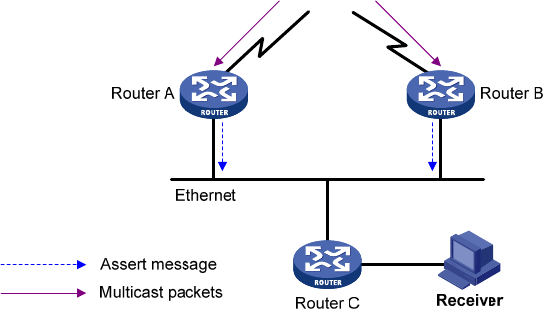
Figure 53 Assert mechanism
As shown in Figure 53, the assert mechanism is as follows:
1. After Router A and Router B receive an (S, G) packet from the upstream node, both routers forward
the packet to the local subnet.
As a result, the downstream node Router C receives two identical multicast packets, and both
Router A and Router B, on their own downstream interfaces, receive a duplicate packet forwarded
by the other.
2. After detecting this condition, both routers send an assert message to all PIM routers (224.0.0.13)
on the local subnet through the interface that received the packet.
The assert message contains the multicast source address (S), the multicast group address (G), and
the preference and metric of the unicast route/MBGP route/multicast static route to the source.
3. The routers compare these parameters, and either Router A or Router B becomes the unique
forwarder of the subsequent (S, G) packets on the shared-media subnet. The comparison process
is as follows:
a. The router with a higher preference to the source wins.
b. If both routers have the same preference to the source, the router with a smaller metric to the
source wins.
c. If a tie exists in route metric to the source, the router with a higher IP address on the
downstream interface wins.
PIM-SM overview
PIM-DM uses the flood-and-prune principle to build SPTs for multicast data distribution. Although an SPT
has the shortest path, it is built with a low efficiency. Therefore the PIM-DM mode is not suitable for large-
and medium-sized networks.
PIM-SM is a type of sparse mode multicast protocol. It uses the pull mode for multicast forwarding, and
is suitable for large-sized and medium-sized networks with sparsely and widely distributed multicast
group members.
The basic implementation of PIM-SM is as follows:
• PIM-SM assumes that no hosts need to receive multicast data. In the PIM-SM mode, routers must
specifically request a particular multicast stream before the data is forwarded to them. The core task
for PIM-SM to implement multicast forwarding will build and maintain RPTs. An RPT is rooted at a










