HP VPN Firewall Appliances NAT and ALG Configuration Guide
5
Easy IP
Easy IP uses the public IP address of an interface on the device as the translated source address to save
IP address resources, and uses ACLs to permit only certain internal IP addresses to be NATed.
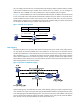
NAT support for VPNs
NAT allows users from different VPNs to access external networks through the same outbound interface,
and allows the VPN users to use the same private address space.
1. Upon receiving a request from an VPN to an external network, NAT replaces the private source IP
address and port number with a public IP address and port number, and records the VPN
information.
2. When the response packet arrives, NAT replaces the public destination IP address and port
number with the internal IP address and port number, and sends the packet to the target VPN.
This feature can also apply to internal servers so that external users can access an internal host of an VPN.
For example, suppose a host in VPN 1 needs to provide Web services for the Internet. It has a private
address of 10.110.1.1. To achieve this purpose, configure NAT to use 202.110.10.20 as the public IP
address of the host so that the Internet users can use this IP address to access Web services on the host.
Address translation
Address translation can be classified into dynamic and static NAT.
Dynamic NAT
A dynamic NAT entry is generated dynamically. Dynamic NAT is implemented by associating an ACL
with an address pool (or the address of an interface in the case of Easy IP). This association defines what
packets can use the addresses in the address pool (or the interface's address) to access the external
network. Dynamic NAT is applicable when a large number of internal users must access external
networks. An IP address is selected from the associated address pool to translate an outgoing packet.
After the session terminates, the selected IP address is released.
Dynamic NAT can meet external access requirements of a large number of users.
Static NAT
Mappings between external and internal network addresses are manually configured. Static NAT can
meet fixed access requirements of a few users.
Low-priority address pool
An address pool is a set of consecutive public IP addresses used for dynamic NAT. A NAT gateway
selects addresses from the address pool and uses them as the translated source IP addresses.
To implement NAT for stateful failover (asymmetric-path), you must configure the same address pool on
both devices so that one device can take over when the other device fails. However, if the two devices
select the same IP address from their address pool and assign the same port number, reverse sessions on
the two devices are the same. As a result, they cannot back up session data.
To solve the problem, the low-priority address pool attribute is introduced to NAT. Configure a
non-low-priority address pool on a device and configure a low-priority address pool on the other device.
The two address pools have the same address range, but have different port number ranges so that the
devices can back up session data.
For more information about stateful failover, see High Availability Configuration Guide.