TMS zl Module Planning and Implementation Guide 2009-08
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Glossary of Acronyms and Abbreviations
- 1.0 Purpose
- 2.0 Intended Audience
- 3.0 Objectives
- 4.0 Prerequisites
- 5.0 Skills
- 6.0 The HP ProCurve Threat Management Services zl Module
- 7.0 Common TMS Security Control Points
- 8.0 Deployment Considerations
- 9.0 Installation and Preparation of the TMS zl Module
- 10.0 Configuration of the TMS zl Module
- 11.0 Using multiple HP ProCurve Threat Management Services zl Modules
- Appendix A – Additional References
- Appendix B – Sample Company Information Assets Spreadsheet
- Sample “Information Assets” tab (See Embedded “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet)
- “Server Network Details” tab (See Embedded “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet)
- “TMS Zones” tab (See Embedded “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet)
- “Firewall Rules” tab (See Embedded “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet)
- /Sample “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet
- Appendix C – Information Gathering Tools
- Appendix D - Updating Switch Software
- Appendix E – Emergency Recovery Process
Page 21
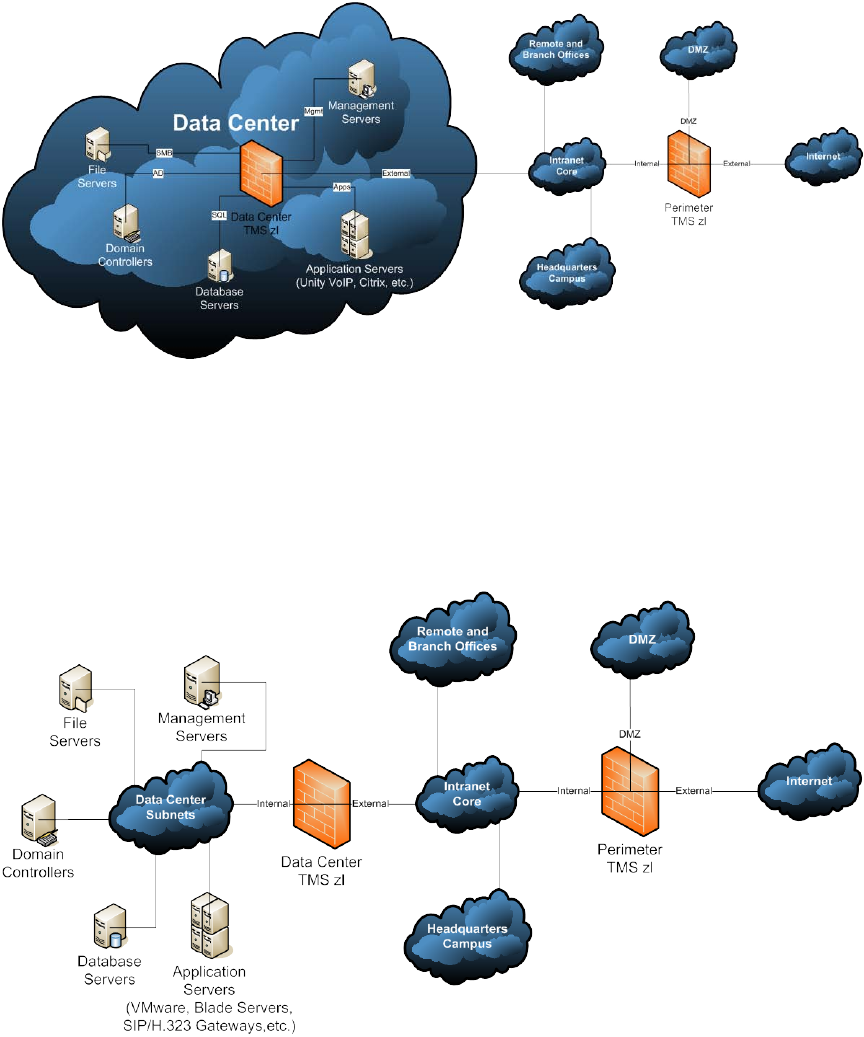
Figure 6: Data Center Compartmentalization Security Control Point
A security enclave is an even higher security area within the enterprise network. The
conversion of the data center into an enclave is simply one of the more obvious
applications of this concept. In the above figure, the data center has been made into an
enclave with compartments within the enclave. In Figure 7, the entire data center has
been converted into an enclave without compartmentalization within the resulting
enclave:
Figure 7: Data Center Enclave Security Control Point
The HP ProCurve Threat Management Services zl Module can:
• Use the firewall feature to compartmentalize different types of servers and the
services they offer using different security zones within the data center and/or limit
traffic coming in to the data center to only that required to use the services offered
by designated servers. For example, SNMP Traps going to the Management
Servers, SMB file sharing traffic headed to the File Servers, Active Directory /










