TMS zl Module Planning and Implementation Guide 2009-08
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Glossary of Acronyms and Abbreviations
- 1.0 Purpose
- 2.0 Intended Audience
- 3.0 Objectives
- 4.0 Prerequisites
- 5.0 Skills
- 6.0 The HP ProCurve Threat Management Services zl Module
- 7.0 Common TMS Security Control Points
- 8.0 Deployment Considerations
- 9.0 Installation and Preparation of the TMS zl Module
- 10.0 Configuration of the TMS zl Module
- 11.0 Using multiple HP ProCurve Threat Management Services zl Modules
- Appendix A – Additional References
- Appendix B – Sample Company Information Assets Spreadsheet
- Sample “Information Assets” tab (See Embedded “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet)
- “Server Network Details” tab (See Embedded “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet)
- “TMS Zones” tab (See Embedded “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet)
- “Firewall Rules” tab (See Embedded “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet)
- /Sample “Company Information Assets” Microsoft Excel 2003 spreadsheet
- Appendix C – Information Gathering Tools
- Appendix D - Updating Switch Software
- Appendix E – Emergency Recovery Process
Page 96
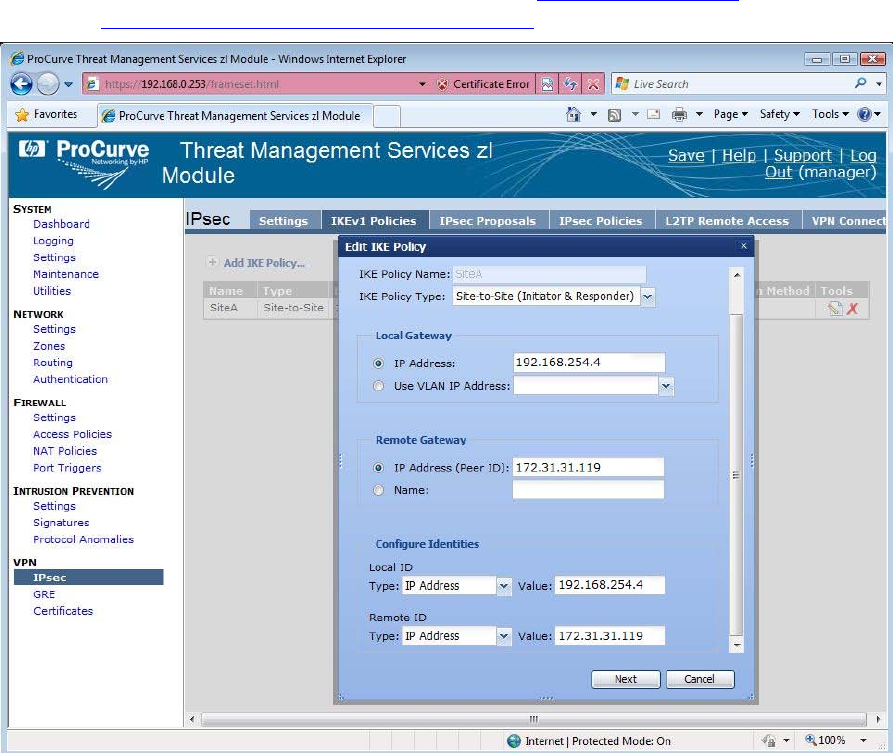
SITE B: We have our firewall setup, but we do not have IPsec configuration in
place yet. We start by creating an IKE policy. We specify site-to-site as the
policy type and enter the TMS zl Module addresses for the Local and Remote
gateways. In our example, we will be using Pre-Shared keys, so we utilize the
same IP addresses for Identities. It is recommended that certificates be used for
customer deployments. See Section C in the HP ProCurve Threat
Management Solution Implementation Guide for more in-depth discussion.