Serial ATA technology, 4th edition
8
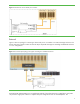
configuration connects a controller to the IO module at each end of a set of cascaded JBODs. Each JBOD contains
a single expander, as shown in Figure 8. This configuration requires half as many IO modules and expanders as
other redundant storage configurations, so it is more economical.
HP dual-path enclosures support both SAS and SATA configurations. Dual-path SATA implementations do not
provide the full redundancy of a dual-domain SAS solution.
Figure 8: This is an example of a dual-path configuration for cascaded JBODs. The “4” notation indicates a 4-lane data path.
Conclusion
With SATA, we offer you affordable configuration options for a broad range of storage applications. For best
performance and reliability, limit the use of SATA hard drives to servers that perform low-workloads (<40%) and to
multi-drive storage configurations such as JBOD and RAID. Limit the use of SATA SSDs to servers performing high
read/low write (70% read/30% write) random data operations. We do not recommend using SATA disk drives in
applications that are not fault-tolerant, require high IOPS, or are mission-critical. The SAS infrastructure gives you the
flexibility to install SAS drives, SATA drives, or both in the same enclosure.