HP Smart Array Controllers and basic RAID performance factors
10
Sequential read performance
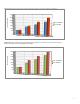
The maximum throughput capability of a drive determines upper limit on sequential performance (see Table 1). The
sequential read performance of an array tends to scale directly with the number of drives in the array.
With larger drive arrays, either the aggregate bandwidth of the SAS links or the PCIe bandwidth limit the sequential read
performance. The smaller bandwidth for either component limits the performance.
RAID 1+0 performance scales more slowly. This occurs because RAID 1+0 mirrors data in addition to striping; therefore,
RAID 1+0 stripes data across fewer drives. It is difficult to get sequential performance from all the drives, and therefore
RAID 1+0 is a little slower.
Figure 6. Scaling of 256 KiB sequential read performance, drive limited until reaching the 4 x 6 GiB SAS bandwidth limit
Configuration: Smart Array P421 controller, 2 GiB cache; 15K SAS drives; maximum measured for queue 1 to 256
Note: RAID 5 measurements with more than 14 drives is for illustrative purposes only. HP does not recommend RAID 5 arrays larger
than 14 drives (depending on tolerance for data loss and type of drive, 14 drives may be too many).
0
500
1,000
1,500
2,000
2,500
4 Drives
8 Drives
12 Drives
16 Drives
RAID 0
RAID 10
RAID 5
RAID 6
MiB/s