HP Smart Array Controllers and basic RAID performance factors
6
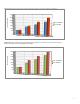
Figure 4. RAID 5 Sequential write performance: Comparing sequential write performance with 512 MiB FBWC versus 2 GiB FBWC.
Optional battery backed or flash backed write cache
In the event of a server or power failure, the data that is in the write cache at the time of the failure could be lost,
resulting in possible data corruption. To avoid possible data loss or corruption, we recommend using flash backed write
cache (FBWC). FBWC uses onboard power from a capacitor to write the cached data to non-volatile flash memory where
it can remain almost indefinitely. FBWC maintains write cache integrity even in the event of a server or power failure.
Earlier versions of the Smart Array controller can use a battery backed write cache (BBWC). BBWC has a battery attached
to maintain the contents of cache module. The batteries are capable of maintaining cache data for up to 72 hours.
Smart Array controllers can ship with FBWC; others have BBWC or FBWC available as options. Without BBWC or FBWC, the
Smart Array controller will not use any of the cache for posted writes or write-back caching. It is possible to override this
default configuration; however, we do not advise doing so. Consequences of using write cache without a BBWC or FBWC
include:
• Data loss or corruption if a server or power failure occurs
• Significant degradation of write performance, particularly in RAID 5 and RAID 6 modes and their derivatives
Drives and performance
Smart Array controllers connect to the drives in an array through SAS-2 physical links (SAS ports):
• New generations of Smart Array P222, P420i, P420, P421, and P721m support up to eight primary SAS ports.
• The Smart Array P220i supports up to four primary SAS ports.
• The Smart Array P822 supports up to twenty-four primary SAS ports.
Each physical link can support a maximum bandwidth of the following:
• 6 GiB/s (600 MiB/s) when 6 GiB/s SAS drives are attached
• 6 GiB/s (600 MiB/s) when 6GiB SATA drives are attached
• 3 GiB/s (300 MiB/s) when 3GiB SATA drives are attached
0
500
1,000
1,500
2,000
2,500
4 Drives
8 Drives
12 Drives
16 Drives
RAID 5; 512MiB FBWC
RAID 5; 2GiB FBWC
MiB/s