HP Smart Array Controllers and basic RAID performance factors
17
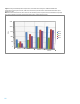
Figure 13. Scaling of 256 KiB sequential write performance; RAID 0/10, drive limited until reaching the 8 x 6 GiB SAS bandwidth limit;
RAID 5/6, drive limited until reaching the controller RAID 5/6 sequential write limit
Configuration: Smart Array P421 controller, 2 GiB cache; 15K SAS drives; queue depth 64; maximum IOPS measured for queue depth
from 1 to 256
Note: RAID 5 measurements with more than 14 drives are for illustrative purposes only. HP does not recommend RAID 5 arrays larger
than 14 drives (depending on tolerance for data loss and type of drive, 14 drives may be too many).
Additional RAID performance characteristics
Many different terms and metrics characterize the performance of Smart Array RAID logical drives. RAID benchmarking
tests often refer to queue depth, throughput, and latency. Understanding how these terms relate will help you
understand them.
Queue depth
Array performance benchmarks are often run at varying queue depths. It is important to understand that in normal use,
queue depth is not a configurable parameter. RAID benchmarking tests can artificially control the queue depth in order
to simulate the effects of controller queue depths growing or shrinking under an application load.
In actual operating environments, a request cached by the write cache is considered completed even though necessary
disk accesses have been deferred and not yet completed. The controller can analyze the commands in the queue to find
more efficient ways to execute them and increase overall throughput for the Smart Array controller.
Throughput versus latency
The Smart Array controller uses various techniques to increase data throughput as queue depth increases. However,
increasing queue depths are an indication that the Smart Array controller is falling behind in processing the drive
commands from the OS and applications. As queue depth increases, latency—the time the OS or application sees it take
to complete a drive request—tends to increase. Applications requiring lower and/or consistent latencies need
environments where queue depths remain low. In general, large queue depths against the Smart Array controller can
indicate a potential controller and drive I/O bottleneck. Adding more drives to the drive array may resolve the issue.
0
500
1,000
1,500
2,000
2,500
3,000
3,500
4,000
4,500
4 Drives
8 Drives
12 Drives
16 Drives
20 Drives
24 Drives
RAID 0
RAID 10
RAID 5
RAID 6
MiB/s