HP StoreEver MSL6480 Tape Library User and Service Guide Addendum (QU625-96016, October 2013)
2 Basic control path and data path failover
With today’s high dependency on access to business information, safe guarded data and limited
backup windows, the reliability of the backup hardware and software is vital. Backup operations
are usually automated, often done at night, and any first pass operator intervention is done remotely.
To assist with these enterprise demands, Hewlett-Packard has introduced two reliability enhancements
to MSL6480 tape libraries with LTO-5 and LTO-6 Fibre Channel tape drives.
• Data path port failover where a standby path is configured for the data path to the tape drive
and activated following link failures.
• Library control path port failover where a second drive is configured to host a standby library
control path that can be activated remotely following link failures.
Failover functionality in the HP LTO-5 tape drives and HP LTO tape libraries transfers the active
path and all settings to the standby path following failures.
HP LTO-5 and LTO-6 data path port failover overview
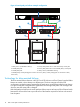
Data path port failover (see “Data path port failover example configuration” (page 13)) may be
configured on each dual-port Fibre Channel tape drive. When data path port failover is configured,
one link is active and is the primary data path. The second link is a standby data path. The drive
will verify that the second link is able to receive a Fibre Channel signal and complete speed
negotiation but the drive will not log into the SAN using the standby link.
NOTE: The LTO-5 half-height drive only has one FC port and does not support data path failover.
The drive monitors the links for errors and following detection of a fault, transfers the fabric identity
(world wide names) and all settings (mode parameters, encryption settings, etc.) over to the standby
link then activates that link. When properly configured the change is minimally disruptive to the
host and does not require any configuration changes on the host or in the backup application.
If no drive commands are outstanding when a failure is detected, the port change happens with
virtually no disruption to the SAN. If a command is outstanding on the link when a failure is detected,
the drive is not able to recover the command so that command will fail but the application will be
able to continue to use the drive on the new path. Many applications are able to recover from a
single command failure as long as the communication path to the drive is not lost.
12 Basic control path and data path failover