HP StoreEver MSL2024, MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096 Tape Libraries User and Service Guide (AK378-96059, December 2012)
Table Of Contents
- User and Service Guide
- Contents
- 1 Features and overview
- Library options
- Interface specifications and requirements for parallel SCSI drives
- Interface specifications and requirements for Fibre Channel drives
- Interface specifications and requirements for SAS drives
- LTO-4 and later generation tape drives and encryption
- Logical libraries
- Control path and data path failover
- Front panel overview
- Back panel overview
- Tape drive back panel overviews
- Tape drive power indicator
- Controller health status indicator
- Power supply back panel (MSL4048, MSL8084, and MSL8096)
- 2 Installing the library
- Preparing the host
- Planning the parallel SCSI configuration
- Planning the SAS configuration
- Planning the Fibre Channel configuration
- Choosing a location
- Unpacking the shipping container
- Identifying product components
- Removing the shipping lock
- Mounting the device in a rack
- Installing the tabletop conversion kit
- Installing tape drives
- Installing a redundant power supply
- Changing the SCSI address (parallel SCSI drives only)
- Connecting the parallel SCSI cable (parallel SCSI devices only)
- Connecting the Fibre Channel cables (Fibre Channel devices only)
- Connecting the SAS cable (SAS devices only)
- Powering on the device
- Configuring the device
- Verifying the connection
- Labeling and loading the tape cartridges
- Verifying the installation
- Configuring additional features
- 3 Tape cartridges and magazines
- 4 Operating the tape library
- Remote management interface (RMI)
- Overview
- Login
- Status pane
- Getting help
- Identity
- Status
- Configuration
- Changing the system configuration
- Changing the drive configuration
- Changing the network configuration
- Configuration: Network Management
- Changing the administrator password
- Setting the date and time
- Setting error log mode
- Setting event notification parameters
- Saving and restoring the device configuration and restoring factory defaults
- Operations
- Support
- MSL2024 Operator control panel (OCP)
- LED indicators
- Library home screen
- Operator control panel buttons
- Understanding the menu structure
- Unlocking the mailslot (Unlock Mailslot)
- Status/Information
- Configuration
- Configuring logical libraries (Status/Information > Set Logical Libraries)
- Changing the administrator password (Configuration > Change Admin Password)
- Setting the number of reserved slots (Configuration > Set Reserved Slot Count)
- Configuring the mailslot (Configuration > Configure Mailslot)
- Bar code reporting format (Configuration > Barcode Format Reporting)
- Changing the SCSI address — parallel SCSI devices (Configuration> Change Drive)
- Changing the drive configuration — Fibre Channel devices (Configuration > Change Drive)
- Setting the master drive (Configuration > Set Master Drive)
- Setting behaviors (Configuration > Library behavior)
- Setting the date and time (Configuration > Library Date/Time)
- Configuring network settings (Configuration > Configure Network Settings)
- Configuring automatic cleaning (Configuration > Configure Auto Cleaning)
- Restoring factory defaults (Configuration > Restore Defaults)
- Saving and restoring the library configuration (Configuration > Save/Restore Configuration)
- Operations
- Unlocking, removing, and replacing magazines (Operations > Unlock Left or Right Magazine)
- Cleaning a tape drive (Operations> Clean Drive)
- Moving tapes in the library (Operations > Move Tape)
- Updating tape cartridge inventory (Operations > Perform Inventory)
- Rebooting the library (Operations> Reboot library)
- Enabling password locks (Operations > Enable Library Password Locks)
- Support
- Powering a drive on or off (Support > Power On/Off Drives)
- Running the demonstration (Support > Run Demo)
- Running the slot to slot test (Support > Run Slot To Slot Test)
- Running the wellness test (Support > Run Wellness Test)
- Upgrading firmware (Support > Library FW Upgrade, Support > Drive FW Upgrade)
- Viewing logs (Support > Library Error Log)
- Downloading a support ticket (Support > Download Support Ticket)
- Forcing the drive to eject a tape (Support > Force Drive To Eject Tape)
- MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096 operator control panel
- Overview
- Using the OCP
- Illustrated menu option and navigation examples
- Info menu
- Configuration menu
- Changing the number of logical libraries (Configuration > Logical Libraries)
- Changing the library configuration (Configuration > Library)
- Changing the drive configuration (Configuration > Drives)
- Changing the network configuration (Configuration > Network)
- Barcode reporting format (Configuration > Barcode Reporting)
- Setting and changing the administrator password (Configuration> Set Admin Password)
- Restore defaults (Configuration > Restore Defaults)
- Setting the library date and time (Configuration > Set Date and Time)
- Saving and restoring the library configuration (Configuration> Save/Restore)
- Operations menu
- Support menu
- Powering drives on and off (Support > Power on/off Drives)
- Cleaning the tape drive (Support > Clean Drive)
- Running tests (Support > Run Tests)
- Viewing logs (Support > View Logs)
- Updating library and drive firmware (Support > FW Upgrade)
- Force ejecting a drive (Support > Force Drive Eject)
- Downloading a support ticket (Support > Support Ticket)
- Rebooting the tape library (Support > Reboot)
- Remote management interface (RMI)
- 5 Troubleshooting
- Detection problems after installing a parallel SCSI device
- Detection problems after installing a SAS device
- Fibre Channel connection problems
- Operation problems
- Performance problems
- Service and repair
- The wellness test
- Error codes
- Warning events
- Configuration change events
- Information events
- Using HP Library & Tape Tools to diagnose problems
- 6 Upgrading and servicing the tape library
- Possible tools needed
- Installing a new tape drive
- Removing and replacing a tape drive
- Removing and replacing a magazine
- Installing a redundant power supply (MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096 only)
- Replacing the power supply (MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096)
- Replacing the library controller (MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096)
- Removing and replacing the base chassis
- 7 Support and other resources
- 8 Documentation feedback
- A Technical specifications
- B Regulatory information
- C Electrostatic discharge
- Glossary
- Index
Technology for data path port failover
The HP LTO-5 and LTO-6 Fibre Channel tape drives configure both ports with identical worldwide
names but only one port will connect to the fabric. By default the port that completes speed
negotiation first will become the active port. If the ports on the drive are connected to different
speed fabric the port connected to the highest speed fabric will typically complete speed negotiation
first. The HP MSL tape libraries that support data path port failover use the default behavior and
do not allow selection of a preferred port.
Technology for control path failover
The HP LTO-5 and LTO-6 Fibre Channel tape drives use a technology called N-Port Identifier
Virtualization (NPIV) which is defined as part of the Fibre Channel standards maintained by the
INCITS/T11 working group (see clause 6) in the FC-LS-2 specification. NPIV allows a single physical
port to connect to a Fibre Channel switch multiple times using multiple node and port names.
Traditional bridged library control path
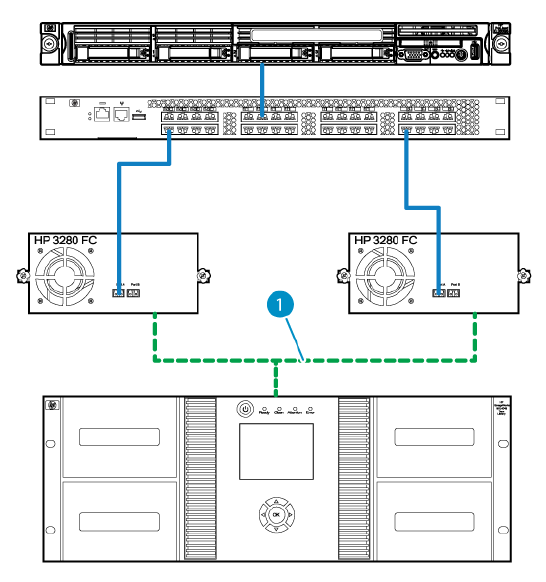
A typical connection for a Fibre Channel tape library using the drive to bridge commands to the
library controller in a two drive tape library is shown in Figure 8 (page 24).
Figure 8 Typical bridged library controller connection
1. Internal connection
In the typical bridge library controller connection each tape drive has one physical link to the SAN
switch and connects to the SAN switch as one Fibre Channel device.
The tape drive hosting the library controller path connects as one Fibre Channel device containing
two logical units. The tape drive is logical unit number zero and the tape library is logical unit
number one. Both devices are considered to be in the same Fibre Channel device which is called
a “Node”. The tape library Fibre Channel node contains a tape drive logical unit and a media
changer logical unit. The logical view of the tape library is shown in Figure 9 (page 25).
24 Features and overview










