HP StoreEver MSL2024, MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096 Tape Libraries User and Service Guide (AK378-96059, December 2012)
Table Of Contents
- User and Service Guide
- Contents
- 1 Features and overview
- Library options
- Interface specifications and requirements for parallel SCSI drives
- Interface specifications and requirements for Fibre Channel drives
- Interface specifications and requirements for SAS drives
- LTO-4 and later generation tape drives and encryption
- Logical libraries
- Control path and data path failover
- Front panel overview
- Back panel overview
- Tape drive back panel overviews
- Tape drive power indicator
- Controller health status indicator
- Power supply back panel (MSL4048, MSL8084, and MSL8096)
- 2 Installing the library
- Preparing the host
- Planning the parallel SCSI configuration
- Planning the SAS configuration
- Planning the Fibre Channel configuration
- Choosing a location
- Unpacking the shipping container
- Identifying product components
- Removing the shipping lock
- Mounting the device in a rack
- Installing the tabletop conversion kit
- Installing tape drives
- Installing a redundant power supply
- Changing the SCSI address (parallel SCSI drives only)
- Connecting the parallel SCSI cable (parallel SCSI devices only)
- Connecting the Fibre Channel cables (Fibre Channel devices only)
- Connecting the SAS cable (SAS devices only)
- Powering on the device
- Configuring the device
- Verifying the connection
- Labeling and loading the tape cartridges
- Verifying the installation
- Configuring additional features
- 3 Tape cartridges and magazines
- 4 Operating the tape library
- Remote management interface (RMI)
- Overview
- Login
- Status pane
- Getting help
- Identity
- Status
- Configuration
- Changing the system configuration
- Changing the drive configuration
- Changing the network configuration
- Configuration: Network Management
- Changing the administrator password
- Setting the date and time
- Setting error log mode
- Setting event notification parameters
- Saving and restoring the device configuration and restoring factory defaults
- Operations
- Support
- MSL2024 Operator control panel (OCP)
- LED indicators
- Library home screen
- Operator control panel buttons
- Understanding the menu structure
- Unlocking the mailslot (Unlock Mailslot)
- Status/Information
- Configuration
- Configuring logical libraries (Status/Information > Set Logical Libraries)
- Changing the administrator password (Configuration > Change Admin Password)
- Setting the number of reserved slots (Configuration > Set Reserved Slot Count)
- Configuring the mailslot (Configuration > Configure Mailslot)
- Bar code reporting format (Configuration > Barcode Format Reporting)
- Changing the SCSI address — parallel SCSI devices (Configuration> Change Drive)
- Changing the drive configuration — Fibre Channel devices (Configuration > Change Drive)
- Setting the master drive (Configuration > Set Master Drive)
- Setting behaviors (Configuration > Library behavior)
- Setting the date and time (Configuration > Library Date/Time)
- Configuring network settings (Configuration > Configure Network Settings)
- Configuring automatic cleaning (Configuration > Configure Auto Cleaning)
- Restoring factory defaults (Configuration > Restore Defaults)
- Saving and restoring the library configuration (Configuration > Save/Restore Configuration)
- Operations
- Unlocking, removing, and replacing magazines (Operations > Unlock Left or Right Magazine)
- Cleaning a tape drive (Operations> Clean Drive)
- Moving tapes in the library (Operations > Move Tape)
- Updating tape cartridge inventory (Operations > Perform Inventory)
- Rebooting the library (Operations> Reboot library)
- Enabling password locks (Operations > Enable Library Password Locks)
- Support
- Powering a drive on or off (Support > Power On/Off Drives)
- Running the demonstration (Support > Run Demo)
- Running the slot to slot test (Support > Run Slot To Slot Test)
- Running the wellness test (Support > Run Wellness Test)
- Upgrading firmware (Support > Library FW Upgrade, Support > Drive FW Upgrade)
- Viewing logs (Support > Library Error Log)
- Downloading a support ticket (Support > Download Support Ticket)
- Forcing the drive to eject a tape (Support > Force Drive To Eject Tape)
- MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096 operator control panel
- Overview
- Using the OCP
- Illustrated menu option and navigation examples
- Info menu
- Configuration menu
- Changing the number of logical libraries (Configuration > Logical Libraries)
- Changing the library configuration (Configuration > Library)
- Changing the drive configuration (Configuration > Drives)
- Changing the network configuration (Configuration > Network)
- Barcode reporting format (Configuration > Barcode Reporting)
- Setting and changing the administrator password (Configuration> Set Admin Password)
- Restore defaults (Configuration > Restore Defaults)
- Setting the library date and time (Configuration > Set Date and Time)
- Saving and restoring the library configuration (Configuration> Save/Restore)
- Operations menu
- Support menu
- Powering drives on and off (Support > Power on/off Drives)
- Cleaning the tape drive (Support > Clean Drive)
- Running tests (Support > Run Tests)
- Viewing logs (Support > View Logs)
- Updating library and drive firmware (Support > FW Upgrade)
- Force ejecting a drive (Support > Force Drive Eject)
- Downloading a support ticket (Support > Support Ticket)
- Rebooting the tape library (Support > Reboot)
- Remote management interface (RMI)
- 5 Troubleshooting
- Detection problems after installing a parallel SCSI device
- Detection problems after installing a SAS device
- Fibre Channel connection problems
- Operation problems
- Performance problems
- Service and repair
- The wellness test
- Error codes
- Warning events
- Configuration change events
- Information events
- Using HP Library & Tape Tools to diagnose problems
- 6 Upgrading and servicing the tape library
- Possible tools needed
- Installing a new tape drive
- Removing and replacing a tape drive
- Removing and replacing a magazine
- Installing a redundant power supply (MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096 only)
- Replacing the power supply (MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096)
- Replacing the library controller (MSL4048, MSL8048, and MSL8096)
- Removing and replacing the base chassis
- 7 Support and other resources
- 8 Documentation feedback
- A Technical specifications
- B Regulatory information
- C Electrostatic discharge
- Glossary
- Index
NOTE: Processor speed numbers as based on Intel x86 type processors. Use the equivalent on
a RISC or other type of processor.
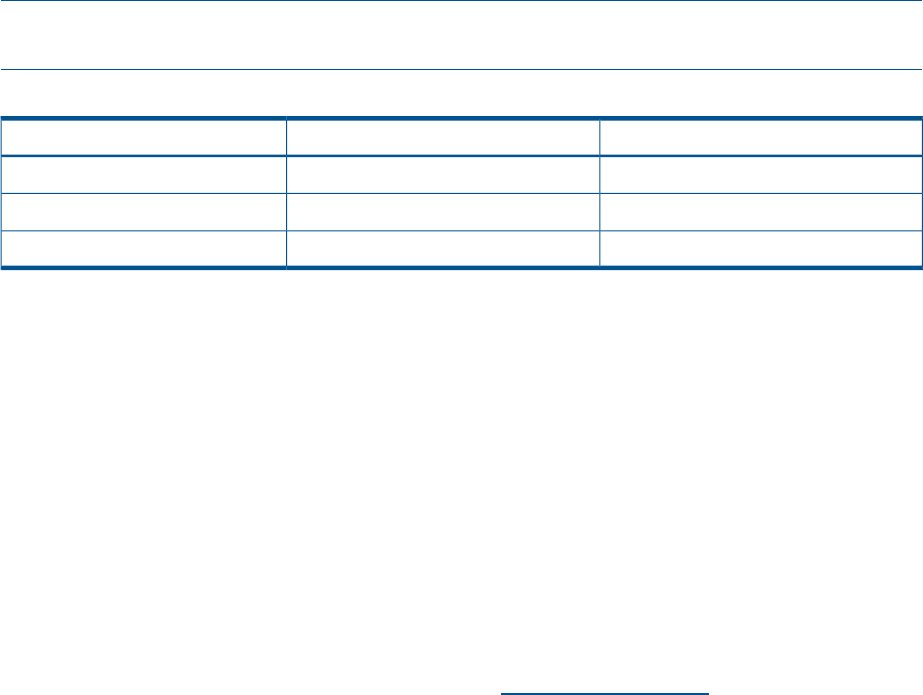
Table 37 Backup server requirements
Processor power/driveMinimum RAM/driveTape drive
2 GHz1 GBLTO-4 HH
3 GHz2 GBLTO-4 FH
4 GHz2 GBLTO-5, LTO-6
In addition to having enough RAM and processing power, ensure that the PCIe bus is at least 64
bit, has a speed of 66 MHz or better, and is not overloaded by too many high-bandwidth cards.
PCIe is preferred.
Backup type
Each type of backup has its own impact on performance, depending on how well it can keep data
streaming to the tape drive.
File-by-file with a full-featured backup application
Performance impact: VARIABLE.
File-by-file backup with a full-featured backup application can be fast enough if the average file
size is at least 64 k and there are not too many fragmented files. Full-featured backup applications
also offer the best speeds for single file restores and allows for backing up only specific data.
Check the compatibility matrix on the EBS website for a list of full-featured backup applications
supported on your operating system for your library: www.hp.com/go/ebs.
If the average file size is less than 64 k or if the file system is very fragmented, file-by-file backup
will have poor performance. If the file system has a lot of fragmentation, use a de-fragmentation
utility to make the files contiguous again. If the average file size is less than 64 k, HP recommends
that you use a sequential/image backup that backups up the hard drive or LUN image instead of
the individual files. The drawback with sequential/image backups is that they may only be able
to restore the entire disk image and not individual files. If they can restore individual files, the
restore operation will be very slow.
File-by-file with a native application
Performance impact: POOR.
Native backup applications based on tar, cpio, NT Backup, etc. do not have the extra features
needed to manage the bandwidth requirements of the faster tape drives and should only be used
to test basic functionality.
To get the best backup and restore performance, use a full-featured backup application. If the
average file size is less than 64 k, use a sequential/image backup for best performance. However,
a sequential/disk image backup might not allow you to restore individual files or the restore process
will be very slow.
Disk image, flash, or sequential
Performance impact: GOOD.
A disk image or sequential backup backs up an entire disk, partition, or LUN by looking at the
disk sector by sector instead of file by file. The entire disk contents is backed up contiguously,
without the disk seeking, which prevents performance degradation caused by small or fragmented
files.
If you are more concerned about backup performance than single-file restore, disk image or
sequential backups can offer a real performance benefit. The disadvantage is that backup and
Performance problems 157










