HP StoreOnce Backup System Concepts and Configuration Guidelines (BB877-90913, November 2013)
The optimum configuration is to use the 10GbE ports for data (NAS shares and Catalyst stores)
and all replication traffic, and the 1GbE ports for the B6000 Management Console. However, this
requires two sub-nets and may not be available to all users.
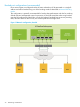
Five network configurations are supported and configured using one of the supplied network
templates, illustrated on the following pages. You must decide which template you intend to use
prior to installation.
Gateway considerations
When the network is configured, you are prompted to provide an IP address for a default gateway,
which will be used to route management and data traffic to and from an external network. Two
of the templates support customer sites with two sub-nets and allow you to route data traffic on one
network and management on the second. For software revision 3.3.0 and greater, for these
templates you are given the opportunity to provide the IP address of a second gateway and specify
which type of traffic it should take.
There are up to three choices when configuring the network (using the StoreOnce CLI):
• No external gateways: If the customer wants to use the HP StoreOnce B6200 Backup System
in a totally isolated network environment, they should not configure an external gateway (the
HP support engineer will simply skip this step during configuration)
• One external gateway: This is the standard configuration with templates 2, 3 and 5, where
data and management traffic are routed to the same subnet, so only one external gateway is
required. When used with templates 1 and 4, the customer must select which subnet (data or
management) will have the ability to communicate with the external gateway.
• Two external gateways (applies to templates 1 and 4 only and for software revision 3.3.0
and greater): This configuration allows both management and data subnets to communicate
with the external network. The IP addresses of the two gateways are provided during the
network configuration. The customer must select whether data or management traffic will use
the 'default' gateway.
NOTE: In this context, 'default' is purely a mechanism to allow the user to specify a gateway for
one type of traffic; the second gateway is automatically used for the other type of traffic.
Examples
• Customer has a 10GbE and a 1GbE network and only wants data to be accessible remotely:
Use Template 1, but configure one gateway only to the 10GbE network for data
• Customer has a 10GbE and a 1GbE network and wants both data and management to be
accessible remotely: Use Template 1 and configure two gateways. Decide whether data or
management should use the 'default' gateway.
• Customer has a 10GbE or a 1GbE network only and wants data and management to be
accessible remotely: Use Template 2, 3 or 4, as appropriate and configure one gateway.
• Customer has a 10GbE or a 1GbE network only and does not want data or management to
be accessible remotely: Use Template 2, 3 or 4, as appropriate and do not configure a
gateway.
NOTE: For software revision 3.3.0 and greater: if the customer wants to have only two 1GbE
network connection from each node in a couplet to their Ethernet switches, they should use Template
5 instead of Template 2 in the above examples.
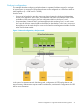
Template 1, uses 10 GbE and 1 GbE sub-nets
Template 1 supports users who have a 10GbE network and a 1GbE network and wish to use
separate sub-nets for data and management. The gateway must be in the same sub-net as the
network that is being used to connect to remote sites. This is normally the data path network.
Supported network configurations (templates) 37