Superdome Servers - I/O Expansion Cabinet Guide, Fifth Edition
Appendix B
Site Requirements
Environmental Requirements
222
Effect of Humidity on ESD Charge Levels
Table B-3 lists charge levels based on personnel activities and humidity levels.
Static Protection Measures
Follow these precautions to minimize possible ESD-induced failures in the computer room:
• Install conductive flooring (conductive adhesive must be used when laying tiles).
• Use conductive wax if waxed floors are necessary.
• Ensure that all equipment and flooring are properly grounded and are at the same ground potential.
• Use conductive tables and chairs.
• Use a grounded wrist strap (or other grounding method) when handling circuit boards.
• Store spare electronic modules in antistatic containers.
• Maintain recommended humidity level and airflow rates in the computer room.
Acoustics
Computer equipment and air conditioning blowers cause computer rooms to be noisy. Ambient noise level in a
computer room can be reduced as follows:
• Dropped ceiling—Cover with a commercial grade of fire-resistant, acoustic rated, fiberglass ceiling tile.
• Sound deadening—Cover the walls with curtains or other sound deadening material.
• Removable partitions—Use foam rubber models for most effectiveness.
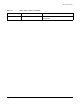
Table B-3 Static Charge Levels and Relative Humidity
Personnel Activity
a
a. Source: B.A. Unger, Electrostatic Discharge Failures of Semiconductor Devices (Bell
Laboratories, 1981)
Humidity
b
and Charge Levels (voltages)
c
b. For the same relative humidity level, a high rate of airflow produces higher static charges than
a low airflow rate.
c. Some data in this table has been extrapolated.
26% 32% 40% 50%
Person walking across a linoleum floor 6,150 V 5,750 V 4,625 V 3,700 V
Person walking across a carpeted floor 18,450 V 17,250 V 13,875 V 11,100 V
Person getting up from a plastic chair 24,600 V 23,000 V 18,500 V 14,800 V